Single point of failure in data storage systems lead to discontinuity and downtime. Downtime is bad for any business. It is costly, leads to loss of reputation and loss of business. In other words, businesses cannot risk it.
Do you want your business to experience downtime because your data storage systems have single point of failure? Of course not!
Before we discuss the solution to single point of failures, let’s define it first and then see how much loss can a business experience due to downtime.
What is a Single Point of Failure in Data Storage Systems?
Single point of failure in data storage systems is an element, component or part of the system whose failure can disable the entire system.
Let’s say a storage appliance has one power supply, this is a single point of failure. If the power supply fails, the entire appliance turns off and the data becomes inaccessible. Similarly, if there’s a single storage head unit / storage controller, its failure will disrupt the entire data storage system.
Likewise, if a data storage system doesn’t have RAID or erasure coding then it also has a single point of failure. If a drive fails, the data in that particular drive is then inaccessible. The system isn’t fault-tolerant. This too results in disruption.
However, it doesn’t affect the entire system. Only the applications and end users using the data in that particular drive are affected.
What’s the Harm in Using Data Storage Systems with Single Point of Failure?
The biggest threat to a business using data storage infrastructure with single point of failure is disruption / outage.
Disruption leads to loss of money, loss of reputation, and loss of business. The end user of today is getting more used to immediate availability of data and services. In order to make that happen, organizations, service providers, and businesses rely on solutions that ensure high availability and high speed access to data. The expectations of users and customers leave no space for disruption / outage or discontinuity.
How bad can disruption be for a business?
When we say financial losses due to disruption, how much are we talking about?
Let’s look at some statistics to gauge how bad disruption can be for a business:
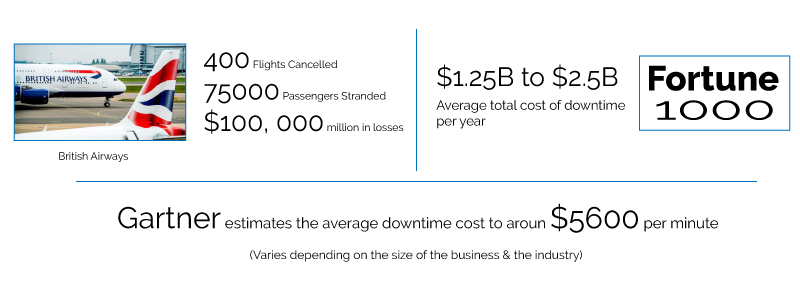
- In May 2017, British Airways had to cancel 400 flights which stranded over 75000 passengers. All due to a power outage caused by a surge of power that happened when a power supply was disconnected and later reconnected. This cost the company around $102.19 million. (Source: NETWORKWORLD)
- For Fortune 1000, the average total cost of downtime per year is $1.25 billion to $2.5 billion. (Source: devops.com)
- Gartner estimates the average cost of downtime to be $5600 per minute. This average increases and decreases depending on the business model and the size of the business.
It’s clear that using storage infrastructure with single point of failure is a risk for businesses.
Why do businesses opt to setup data storage systems with single point of failure? The most common reason is due to the cost.
Data storage appliances without single point of failure are expensive. Alternatives to expensive high availability or redundant solutions tend to be complex or more expensive. (We discuss some of these alternatives later in this blog)
So far, we’ve defined single point of failure in data storage systems and we know that single point of failures present a risk of disruption. Disruption tends to be very expensive for businesses. In other words, we are now familiar with the problem. What’s the solution?
How can enterprise data storage systems be free of single point of failure?
What can businesses do to make sure they don’t have to deal with disruption?
Data Storage Solutions without Single Point of Failure
There are quite a few solutions that can help remove single point of failure from data storage systems.
StoneFly caters to the storage requirements of enterprise customers. Our customers include organizations from healthcare, banking, entertainment, and many other industries that cannot tolerate delay, disruption or discontinuity.
We have been delivering storage solutions for these industries for over two decades. Regular feedback from our customers have helped us develop technology and expertise that easily help with challenges like single point of failure.
What options do we have for single point of failure-free data storage?
We have High Availability (HA) appliance configuration in all of our storage systems. Our storage appliances are also cloud-enabled; fully hybrid data storage.
How do our HA appliances or hybrid appliances help with single point of failure? Let’s take a look at both of them.
StoneFly High Availability (HA) Cluster Architecture
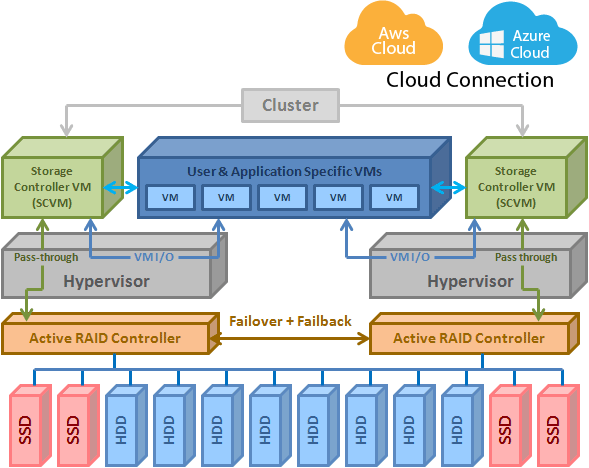
StoneFly HA appliances comprise of at least 2 x 1U storage head units (or 1 x 2U storage head unit) and at least one RAID subsystem.

1U Storage Head Unit

2U Storage Head Unit
The two storage head units offer multi-path access to the RAID subsystems. This makes sure that there’s no single point of failure in the data storage system. Each appliance, storage head units and the RAID subsystem, has redundant power supplies. Users can choose from RAID levels ranging from 0 to 60 and they can also opt to configure erasure coding.
How does RAID help with data redundancy? Learn how RAID technology works: Click here to learn about RAID.
How does erasure coding make the storage system fault tolerant? Click here to learn about Erasure Coding.
In our hyperconverged appliance (StoneFly USS™), users deploy two virtualization layers (hypervisors). This practice improves the fault tolerance of the storage system.
Similarly, the management software (StoneFly SCVM™) also has two instances running. In the event one fails, or the relevant storage head unit fails, the system continues to operate without downtime.
Our storage systems are enterprise-grade solutions. They are highly scalable, redundant, and robust. StoneFly storage solutions can scale from a few terabytes to petabytes in storage capacity.
StoneFly High Availability Petabyte Storage Solutions
Is the HA appliance configuration available for petabyte storage solutions?
Our petabyte storage solutions add another layer of redundancy with modular RAID units.
StoneFly petabyte storage solutions are available in HA Modular (HA-M) configuration. Similar to HA configuration, the HA-M configuration has at least 2 x 1U storage head units (or 1 x 2U storage head unit) and at least one EBOD along with a separate RAID head unit.
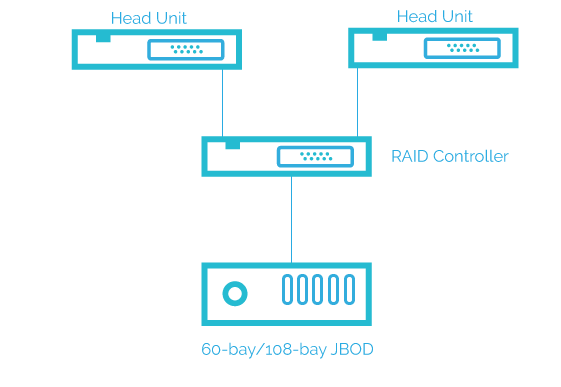
Other than the high availability configuration, StoneFly storage and backup appliances also support “Dual Node Shared Nothing” configuration.
What is the Dual Node Shared Nothing configuration and how does it help with single point of failure in data storage systems?
StoneFly “Dual Node Shared Nothing” Storage Appliance Configuration
The Dual Node Shared Nothing configuration comprises of two identical appliance nodes. Each appliance node has a storage controller, RAID controller, and storage drives (SAS and / or SSDs).
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.

In order to mirror the data stored in one node on the second node, our appliances use synchronous / real-time replication.
With synchronous replication, the data is shared between both nodes in real time as it’s written.
This practice makes sure that there’s no disruption or outage even if an entire appliance node fails. The Dual Node Shared Nothing configuration is fit for enterprise IT environments that require very low RTOs (Recovery Time Objectives) and RPOs (Recovery Point Objectives).
What are RTOs and RPOs? Click here to learn about RTPOs.
The HA appliance and the Dual Node Shared Nothing is an on-premises / in-house redundant storage option. If your data protection practice needs you to setup an offsite storage repository, then neither of these two options will work for your business.
So what options do we have to help your business with single point of failure? For such businesses, we have the following solutions:
- Asynchronous Replication
- Hybrid Data Storage Solutions
- Cloud Disaster Recovery
Reducing the Risk of Single Point of Failure in Data Storage Systems with Asynchronous Replication
StoneFly storage and backup appliances support asynchronous replication. With asynchronous replication, businesses can setup offsite redundant storage appliance.
Asynchronous replication enables businesses to create replicas of mission-critical data as per a pre-defined schedule. This makes asynchronous replication a good choice for long distance secondary storage systems.
Unlike synchronous replication, asynchronous replication is scheduled. That implies that IT administrators can schedule storage replication jobs on the time of day when bandwidth consumption is low; for example at the end of the work day. This also helps IT administrators to control bandwidth consumption and reduce storage costs.
The drawback of asynchronous replication is that since it’s scheduled and not real-time, it has higher RTPOs, depending on when the replication jobs are scheduled.
StoneFly offers a number of storage systems for businesses looking to leverage asynchronous replication and remove single point of failure from their data storage infrastructures.
I have a primary storage infrastructure but I need a secondary storage system
For such use-cases, businesses can leverage any one of StoneFly’s data storage solutions.
- StoneFly SSO™ NAS – highly scalable file-level storage appliance
- StoneFly ISC™ SAN – high performance block-level iSCSI appliance
- StoneFly USS™ – hyper converged storage appliance
- StoneFly USO™ – unified converged hyperscale storage appliance
Learn more about StoneFly storage appliances by clicking here.
Depending on their usage, businesses can choose any of the above and have it setup as an offsite storage infrastructure to ensure a single point of failure free storage system.
I have both primary & secondary storage infrastructure. I just need asynchronous replication.
For this use-case, we offer a virtual storage gateway that enables users to add asynchronous replication and a number of other data services that optimize the enterprise data storage experience.
For businesses running their storage on bare-metal or storage appliances without hypervisors, we offer StoneFly StoneFusion™. StoneFusion is our patented software-defined storage that can be configured as a virtual gateway appliance. Users can add data services like asynchronous replication, data encryption, deduplication, erasure coding, and many more.
If the enterprise IT environment is running hyper converged storage, then businesses can leverage StoneFly’s software defined storage solution SCVM™. SCVM is StoneFusion deployed as a Virtual Machine (VM). It has all the features of StoneFusion and enables users to integrate asynchronous replication and a number of other data services as well.
Leveraging Hybrid Data Storage Solutions to Remove Single Point of Failure
There are two types of hybrid data storage solutions. When a storage appliance is configured with different types of drives (enterprise hard drives and flash drives), it’s called a hybrid storage system. The second type is cloud-enabled storage appliances. They are called hybrid because they combine the speed and performance of on-premises infrastructure with the scalability of the cloud.
In the context of removing single point of failure from a data storage system, we’re referring to the second kind of hybrid storage solutions.
How does hybrid data storage solution help with single point of failure?
Users can create copies of their data in the cloud. In the event of hardware failure, they can use the cloud copies and continue operating.
Businesses with budget restrictions can leverage hybrid data storage solutions. Instead of purchasing and setting up a dedicated secondary storage or setting up an on-premises Dual Node Shared Nothing configuration; they can integrate the cloud.
How do hybrid data storage solutions compare to Dual Node Shared Nothing & HA appliance configurations?
In comparison to Dual Node Shared Nothing or HA configuration, hybrid storage solutions aren’t as fast when it comes to recovering from downtime.
Dual Node Shared Nothing and HA appliances make sure that the user doesn’t experience any disruption at all. While users of hybrid data storage solutions have to wait until they can recover the data from the cloud.
Organizations that can tolerate a little delay and have budget restraints can use hybrid data storage solutions to reduce the risk of downtime due to single point of failure.
How much time would it take for a business to recover from downtime if they’re using hybrid data storage solutions?
That depends on how the business has configured the cloud storage repository. It’ll take a lot more time to access data from an archival storage tier than it will take to use it from a hot storage tier.
While using cool tiers or archival tiers is cost effective; especially if the user is not accessing data frequently. Consequently, it’s slower than hot tier because it’s not built for speed; rather it’s built for cost effectiveness and long term data retention.
Did you know that all StoneFly storage solutions can be configured as hybrid data storage solutions?
All StoneFly storage appliances are pre-configured with StoneFly StoneFusion. StoneFusion can be configured as a virtual cloud gateway to Microsoft Azure, AWS, StoneFly cloud and any other S3 compatible cloud.
While StoneFly storage appliances are modular, redundant, and robust infrastructures. Users can add another layer of redundancy by integrating the cloud and make sure that even if the hardware fails, the business continues operating with minimum disruption.
Using Cloud Disaster Recovery to Reduce the Risk of Downtime Due to Single Point of Failure
Using cloud disaster recovery to remove single point of failure from data storage systems is similar in function to hybrid data storage systems. However, there’s one big difference. Cloud disaster recovery solutions are built to reduce RTPOs.
This implies that unlike hybrid data storage solutions that may take more time to recover. Cloud disaster recovery solutions are purpose-built to reduce the time it takes to recover and get the business back up and running.
How long does it take to recover from downtime using cloud disaster recovery solutions?
The answer to that depends on the volume of data that needs to be recovered. The larger the data, the more time it will take.
The speed of recovery also greatly depends on the available bandwidth. If there’s more bandwidth available, then data transfer will be faster and recover will be faster. If there are limitations on how much bandwidth a business can use, then using cloud disaster recovery solutions as a means to recover from downtime is not a good idea.
Cloud disaster recovery solutions and cloud storage solutions rely a lot on available bandwidth. Before integrating them, businesses must analyze the bandwidth they’ll need and the volumes of data they’ll need to transfer.
Conclusion
Single point of failure is bad for business. By using data storage solutions with single point of failure, businesses risk discontinuity and downtime. Downtime is very costly for any business, regardless of its size and industry.
That’s why businesses need to deploy data storage solutions that are redundant, robust, and have no single point of failure.
To help businesses setup reliable data storage solutions that are resistant to downtime, StoneFly offers a number of on-premises and virtual solutions.
Single point of failure and downtime shouldn’t be a concern for your business.
Talk to our storage experts and let them help you with single point of failure.
You can call us at (510) 265 1616.
You can also send us an email at sales@staging.stonefly.com









