Optimizing storage efficiency is paramount. One key technology that addresses this need is data deduplication. By eliminating redundant data, businesses can significantly reduce storage consumption, leading to lower costs and improved return on investment. Storage optimization features like deduplication have become essential for businesses grappling with ever-growing data volumes.
In this blog, we will explore the power of data deduplication and its impact on storage efficiency.
What is Data Deduplication?
Data deduplication is a technique used to eliminate redundant or duplicate data within a storage system. It identifies and removes identical data segments, leaving only one copy of each segment and replacing subsequent occurrences with references to the original copy.
By eliminating data duplication, deduplication reduces storage space requirements, improves data transfer efficiency, and optimizes backup and recovery processes. It is commonly employed in backup systems, primary storage systems, and data archival solutions to maximize storage efficiency and minimize costs.
In light of this explanation, you must be wondering how often do these duplicate byte patterns occur and how much of an impact can
How often do these duplicate byte patterns occur?
Same byte patterns occur dozens, hundreds or even thousands of times, depending on the scale of the data. For your reference, consider the
How much of an impact can dedup make in terms of storage efficiency?
Data deduplication can have a significant impact on storage efficiency, resulting in substantial space savings. The level of deduplication achieved depends on factors such as data types, redundancy levels, and the effectiveness of the deduplication algorithm.
In real-world scenarios, deduplication ratios can vary widely. For instance, organizations dealing with backup data may experience deduplication ratios ranging from 5:1 to 20:1 or even higher. This means that for every 5 to 20 units of original data, only 1 unit of unique data needs to be stored. Such ratios demonstrate the potential storage savings achievable with deduplication.
To put this into perspective, let’s consider an example. Suppose a company has 100 terabytes (TB) of data that needs to be backed up regularly. Without deduplication, this would require 100 TB of storage capacity. However, with an average deduplication ratio of 10:1, the effective storage required would be reduced to 10 TB, resulting in a space savings of 90%.
What deduplication ratios do StoneFly appliances support?
StoneFly appliances provide flexibility in deduplication ratios, allowing organizations to choose the most suitable option based on their specific needs. Depending on the selected hardware specifications, StoneFly appliances can be configured to achieve deduplication ratios of 4k, 32k, or even 64k. This customization empowers businesses to fine-tune their deduplication settings to strike the right balance between storage efficiency and performance.
By leveraging data deduplication, organizations can achieve significant storage savings, optimize resource utilization, and reduce costs associated with storage infrastructure expansion and maintenance. StoneFly’s appliances offer the added advantage of customizable deduplication ratios, enabling businesses to tailor the deduplication process to their unique requirements.
When to Use Data Deduplication (Deduplication Use-Cases)
Data deduplication is a valuable technique for optimizing storage efficiency and reducing data redundancy. Companies should consider implementing data deduplication in the following scenarios:
- Reducing Storage Costs: When organizations face challenges with limited storage capacity or escalating storage costs, data deduplication can help address these issues. By identifying and eliminating duplicate data across the storage environment, companies can significantly reduce the amount of physical storage required, resulting in cost savings and more efficient resource utilization.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Data deduplication plays a crucial role in backup and disaster recovery strategies. By eliminating redundant data across multiple backups, it minimizes the storage footprint and reduces backup windows. This allows for faster backups, more efficient replication, and accelerated recovery times in case of data loss or system failures.
- Virtualized Environments: Virtualization environments often encounter data duplication due to multiple virtual machines using similar operating systems, applications, or shared templates. Implementing data deduplication in these environments can optimize storage utilization by identifying and eliminating duplicate data blocks, resulting in significant storage savings and improved overall performance.
- File Sharing and Collaboration: Companies that heavily rely on file sharing and collaboration platforms, such as NAS appliances, can benefit from data deduplication. As users share files, attachments, and documents, data deduplication eliminates duplicate content, reducing storage requirements and enhancing data transfer efficiency. This leads to improved collaboration experiences and optimized utilization of storage resources.
- Archiving and Long-Term Retention: Organizations that maintain large archives or require long-term data retention can leverage data deduplication to reduce the storage footprint of archived data. By identifying and removing duplicate data within archives, companies can optimize storage utilization while still ensuring data integrity and accessibility for future retrieval.
What are the different types of data deduplication?
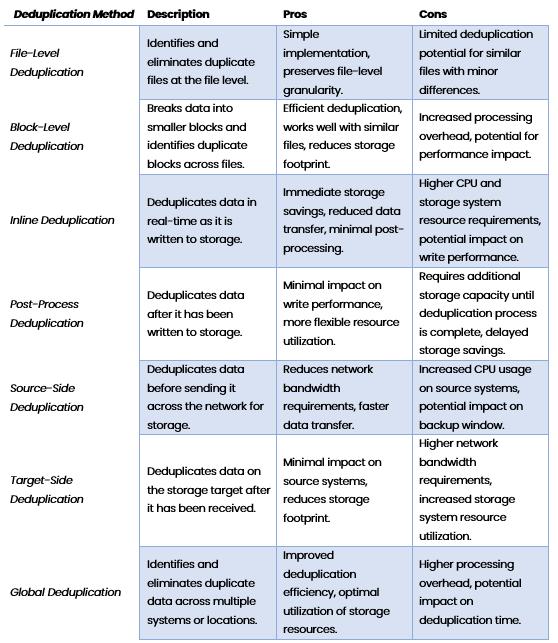
There are seven different types of data deduplication methods, each offering unique benefits and considerations. Let’s explore these different techniques in detail:
- File-Level Deduplication: This method identifies duplicate files based on their content, regardless of their file names or locations. By comparing file contents, identical files are recognized and only a single copy is stored, saving storage space.
- Block-Level Deduplication: In block-level deduplication, data is divided into small blocks, typically a few kilobytes in size. These blocks are compared, and duplicate blocks are replaced with references to a single stored block. This approach offers higher deduplication ratios and reduces storage needs.
- Inline Deduplication: Inline deduplication occurs in real-time as data is being written to the storage system. Duplicate data is identified and eliminated before it is stored, reducing the amount of data transferred and stored. This approach minimizes storage requirements and improves data transfer efficiency.
- Post-Process Deduplication: Unlike inline deduplication, post-process deduplication identifies and removes duplicates after the data has been written to the storage system. This approach allows for faster data ingestion and can be more suitable for high-performance systems.
- Source-Side Deduplication: Source-side deduplication takes place before data is sent across the network to the storage system. By identifying and eliminating duplicate data at the source, it reduces the amount of data transferred, optimizing bandwidth usage and reducing storage requirements.
- Target-Side Deduplication: Target-side deduplication occurs after data has been transferred to the storage system. Duplicate data is identified and eliminated, maximizing storage capacity and reducing storage costs. This approach is commonly used in backup and recovery solutions.
- Global Deduplication: Global deduplication enables deduplication across multiple storage systems or devices, eliminating duplicates across the entire data environment. It ensures maximum efficiency by identifying and removing duplicates across all storage resources.
By employing these different types of data deduplication techniques, organizations can significantly reduce storage costs, improve data management efficiency, and enhance overall system performance. The choice of deduplication method depends on specific requirements, storage architecture, and data workload characteristics.
Comparing Data Deduplication Deployment Methods
It’s important to consider various factors such as data characteristics, system requirements, performance impact, and storage savings when selecting the appropriate deduplication method for a specific environment.
Comparison: Deduplication versus Compression
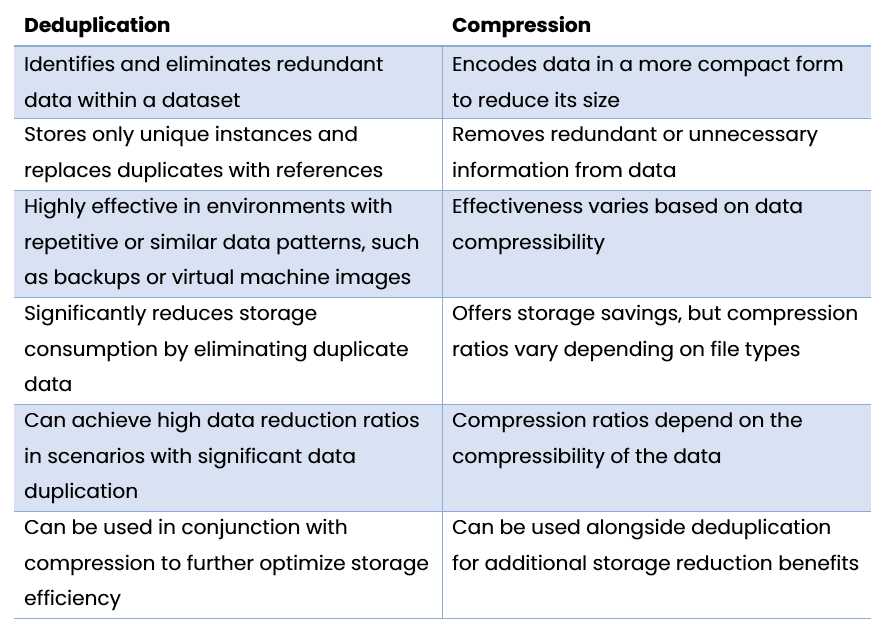
Deduplication and compression are two distinct data reduction techniques, each with its own advantages and considerations.
Deduplication focuses on identifying and eliminating redundant data within a dataset, storing only unique instances and replacing duplicates with references. This approach significantly reduces storage consumption, particularly in environments with repetitive or similar data patterns, such as backups or virtual machine images.
On the other hand, compression involves encoding data in a more compact form to reduce its size. It leverages algorithms to remove redundant or unnecessary information and store data in a compressed format. While compression offers storage savings, its effectiveness varies based on the data’s compressibility. Certain file types, such as text or XML, typically achieve higher compression ratios compared to already compressed files like multimedia formats.
Both deduplication and compression techniques can be used independently or in combination, depending on the specific use case and requirements. By employing a combination of both techniques, organizations can achieve even greater storage efficiency and maximize data reduction benefits.
Conclusion
Data deduplication stands as a powerful solution for enhancing storage efficiency in the face of escalating data volumes. By eliminating redundant data, businesses can optimize storage utilization, reduce costs, and improve overall performance. The ability to store more data in less space offers significant advantages, enabling organizations to maximize their resources and make informed decisions.
With the continuous growth of data, embracing deduplication becomes imperative for businesses seeking to achieve optimal storage efficiency and stay ahead in the data-driven landscape.