Increased Bandwidth does not Equate Increased Throughput – Long Fat Network
Consider an enterprise with multiple branches setup at geographically separated locations. The data transfer between these branches utilizes a WAN network. For large chunks of data, this network introduces latency. Despite, bandwidth throttling the problem persists so the enterprise decides to expand their bandwidth. This removes any bottlenecks from before but it doesn’t increase the data transfer rate. That’s because increased bandwidth is not the same as increased throughput. By simply increasing the bandwidth, the enterprise ends up with a Long Fat Network (LFN).
For instance, if water is the data and bandwidth is the pipe, then the enterprise simply increased the space of the pipe. It didn’t do anything to the speed of the water. The only thing that did was make the flow of water smoother.
Instead of unnecessarily spending on their bandwidth expansion, the enterprise should acquire a WAN optimizer.
That clears up the bit about increased bandwidth but it doesn’t answer the question: Where does this latency come from in a WAN network? Let’s look at that.
Where does latency come from in a WAN Network?
Latency is caused due to our reliance on very effective but very old protocols that were developed for different applications and use. The latency in question is caused due to TCP or Transmission Control Protocol. It is a mainstream transport protocol that most of the internet relies on.
TCP provides various mechanisms that enable effective control of the flow of packets across a network. For instance, it enables network administrators to know when data packets are lost and when to retransmit them. TCP is also capable of identifying when the network is congested and needs bandwidth throttling. Basically, TCP delivers a range of necessary services. In order to do so, the sender needs to receive an acknowledgment packet or ACK packet from the receiver.
This ACK packet is the culprit that causes the latency experienced in WAN networks. In a larger network, as the round trip time grows, the data transfer rate across a TCP drops down. TCP keeps waiting for the ACK packet and limits data flow. This is why even with a larger bandwidth, you get less throughput and experience latency.
This is where StoneFly’s WAN optimizer: StoneWAN, comes in. A thing to note here is that StoneWAN isn’t exclusively compatible with TCP. It also supports FTP, NFS, CIFS and HTTP protocols.
StoneWAN: Efficient and Secure Bandwidth Accelerator for the Multi-branch Enterprise
StoneWAN delivers enterprise level services to ensure higher data transfer rates between geographically separated branch offices. StoneWAN operates at layer 2 of the network.
Consider a setup with two branch offices and their respective gateways. The software-defined (SD) WAN are added behind the router on each side. This implies that the SD-WAN are integrated between the gateway and the machines on each side. This setup enables it to be integrated in any existing branch office without disruption or discontinuation and without affecting the existing network configuration.
How StoneFly WAN Accelerator works?
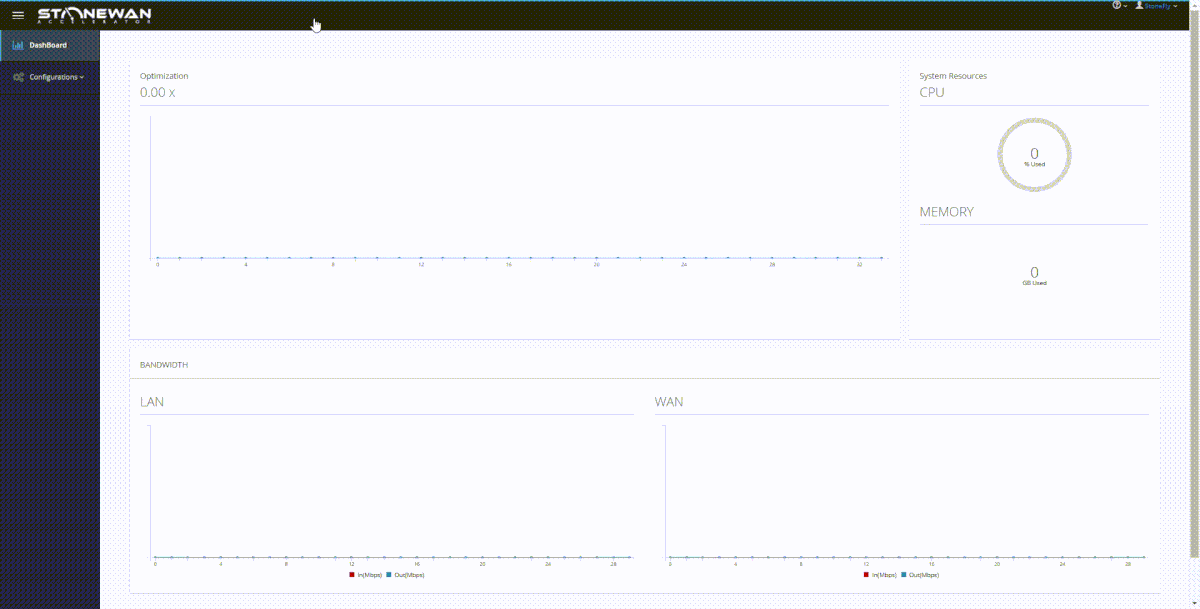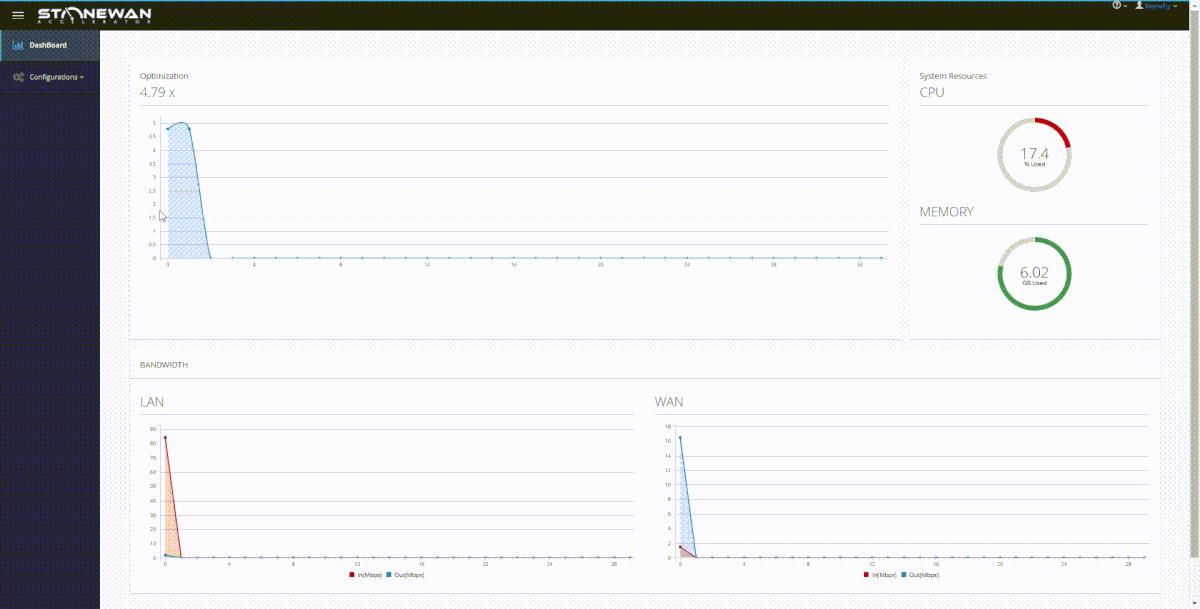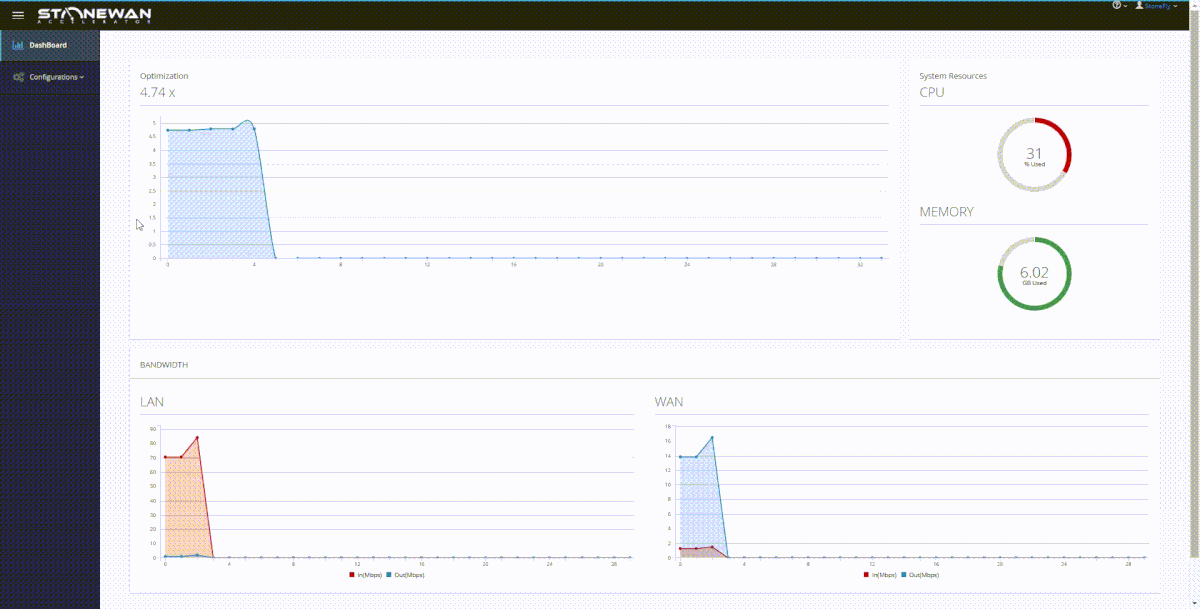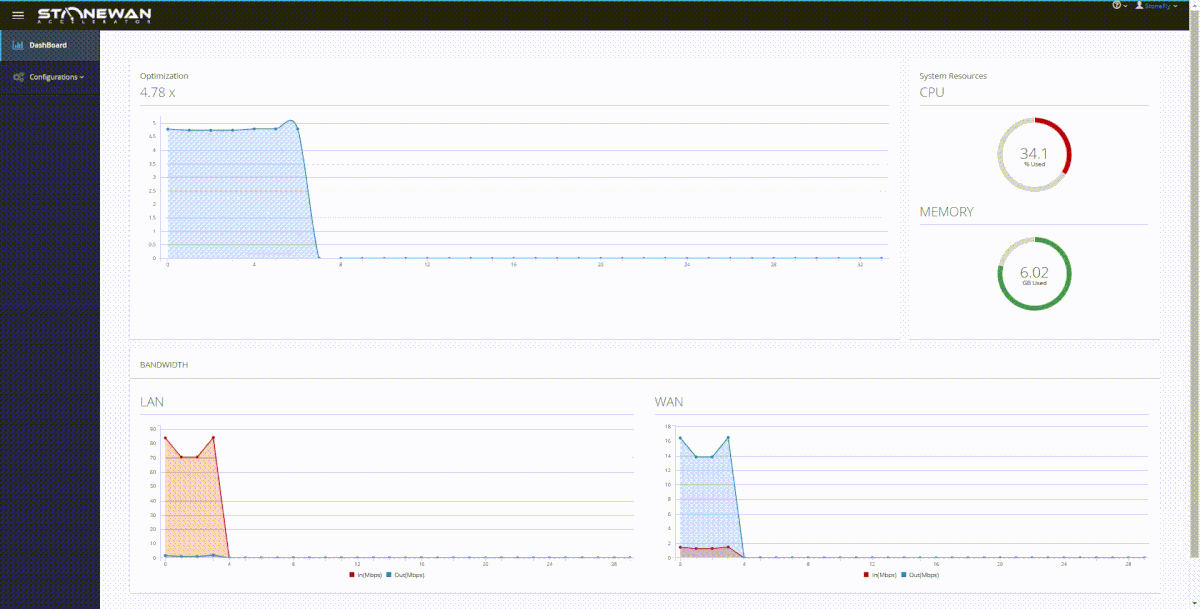
StoneWAN performs data transfer acceleration in a twofold process:
- Compression
- Dynamic Deduplication.
StoneWAN performs compression and dynamic deduplication on each packet received at the appliance.
If we are to consider the example of the two branch offices again; this is how things go. When a service or data is accessed from the source office, the TCP packet moves from the machine and is first received at the appliance. That’s because of the setup; the StoneWAN appliance sits between the machine and the source gateway.
This TCP packet is first compressed and deduped at the source end, decreasing the packet size by a considerable amount. The deduped packet is then sent over the network. As it has been reduced in size, it moves a lot faster than its original counterpart.
At the receiving end, the gateway receives the deduped packet and it is then received by the StoneWAN appliance between the receiving gateway and the machine. This WAN accelerator then decompresses the file and restores it to its original size, sending it forward to the receiving machine.
Using these data compression techniques, the multi-branch enterprise gains:
- Enhanced Data Transfer speed.
- Optimized Bandwidth Utilization.
- Reduced cost implications due to effective bandwidth utilization.
StoneWAN: Software-defined WAN and Physical Appliance
StoneFly’s StoneWAN is available as a software-defined WAN and you can also get a physical appliance to integrate with your setup. To learn more, contact us, talk to our experts and schedule a demo.










