The application of multi-cloud computing cloud might be tough but the idea of multi-cloud is simple. Multi-cloud, in simple terms, means the utilization of more than one public or private cloud(s). Enterprise data requirements change with time and service provider continue to innovative ways to address these requirements. Multi-cloud computing model is a rather simple concept that delivers redundancy and prevents vendor lock-ins. Let’s discuss the computing model in a bit more detail.
What is multi-cloud?
Multi-cloud, as the term suggests, is the deployment of workloads in more than one cloud; these can be public clouds or private clouds. The computing model doesn’t suggest an entire collection of services offered by various cloud service providers; rather, even an environment using two clouds is classified as a multi-cloud setup.
Multi-cloud refers to the implementation of multiple SaaS (Software as a Service) and PaaS (Platform as a service) cloud offerings. There is a highly competitive market in terms of cloud technology. This industry requires continuous innovative options.
When an enterprise uses more than one cloud (such as Microsoft Azure, AWS, OpenStack etc.) for storage, backup or any other purpose; that’s referred to as multi-cloud computing. For instance, an enterprise may be using Amazon Web Services for data storage and then creating replicas in Microsoft Azure in order to ensure data recoverability. This feels like an effective multi-cloud solution but it requires rigorous management and an efficient multi-cloud strategy.

Benefits of Multi-cloud Solutions:
There are times when one vendor is suitable for your enterprise. However this varies from enterprise to enterprise. Sometimes, an enterprise comes across solutions of a different vendor that are beneficial but not available with the current vendor and vendor lock-in prevents access to that service. Although a multi-cloud setup needs some additional management tools it can allow your organization to avail quite a few benefits:
- Prevents vendor lock-in: Due to the flexibility that multi-cloud computing model delivers, businesses are no longer restricted by vendor lock-ins. Enterprise IT environments can choose between the available services of different vendors and pick the best suitable for their requirements.
- Cost efficiency: Without vendor lock-ins, businesses don’t have to pay for that one service of your vendor that’s too expensive. If you can find a better cost effective solution, multi-cloud computing model enables you to acquire it and set it up. This results in a rather complex contract situation; however, if done right, it can enhance overall cost efficiency.
- Improved Availability and Performance: Multi-cloud computing model allows your infrastructure to have data redundancy to optimize fault tolerance and improve availability and performance.
- Compliance: Multi-cloud computing model delivers data redundancy and taps into the security protocols of more than one cloud(s); this facilitates businesses in pursuing industry compliance.
- Improved Mobility: In terms of acquisition and setup, cloud based services have no comparison. Multi-cloud services are no exception. They are easier to deploy and facilitate enhanced accessibility for the Enterprise IT environment.
- Business Continuity/High Availability: Multi-cloud computing model delivers data redundancy ensuring data availability and business continuity. If an IT environment relies on a sole vendor and that vendor experiences downtime or an outage, the IT environment also suffers. With multi-cloud computing model, the IT environment can continue to operate even when one or more of the vendors go down.
- Improves geo-presence: By using multiple clouds you have more options for geographic targeting to manage the latency issues and address data sovereignty.
Considerations for deploying multi-cloud computing model:
When you are going to adapt multi cloud solutions, there are somethings which you should keep in mind and you should consider. Few of them are mentioned below:
- Prevention form Vendor Lock-in:
IT environments have been battling vendor lock-ins for many years. In this world it’s not a smart choice to be dependent on one cloud provider. Multi-cloud allows you to incorporate more than one cloud providers and utilize services that best suit your data requirements, regardless of the vendor.
- Acquiring appropriate IT experts: Each cloud has its own data encryption protocols and compatibility issues. An expert well adept to a specific cloud may not be knowledgeable when it comes to handling a different cloud environment. If your IT infrastructure is deploying a multi-cloud environment, then you have to set up a team of experts that are familiar with all of the clouds you are going to use.
- Financial considerations: Multi-cloud environments are tough and complex to manage. They can be costly as well. The prices vary as multi-clouds comprise of different services and payment models.
- Connectivity: One of the key considerations is the connectivity. Even if you’re deploying a single cloud environment, connectivity has an integral role in effective data management and handling. Without a fast enough network and large enough bandwidth, you can be looking at issues such as bottlenecks, lag, and delayed responses.
Why do enterprises need multi-cloud computing model?
One of the major pros of a multi-cloud strategy is the unified deployment of different environments. This makes the multi-cloud computing model a great choice for DevOps and testing environments.
With a multi-cloud environment, DevOps can test applications and backup and disaster recovery plans without setting up expensive and dedicated hardware.
Furthermore, multi-cloud computing model allows enterprises to have cross cloud storage where they store their data in different clouds instead of just one which allow easy backup and archiving. An enterprise can utilize different cloud services as required and pay for each service as they go.
The multi-cloud model also helps in disaster recovery situations by taking data backups from multiple clouds and storing them at a single location. This ensures that, if any one of the backups is compromised, other backup will be available to restore and serve as a fail safe.
Multi-cloud versus hybrid cloud: What’s the difference?
There’s a fine line between multi-cloud and hybrid cloud computing models. Sometimes, one is mixed with the other.
Multi-clouds in its simplest form is the utilization of more than one cloud. However, in this computing model, the kind of cloud remains the same. The use of multiple public clouds like Azure, AWS, Google etc. qualifies as a multi-cloud environment.
Hybrid-cloud, not to be confused with hybrid infrastructure or hybrid solutions, is the utilization of different kinds of clouds. For instance, an IT infrastructure has their own private cloud setup and they’re also using Microsoft Azure or AWS; this is a hybrid cloud setup.


Multi-Cloud Computing Trends:
According to the survey of EMA (Enterprise Management Associates) the percentage of enterprises that have a strategy to use multiple clouds grew to 85 percent (vs. 82 percent in 2016).
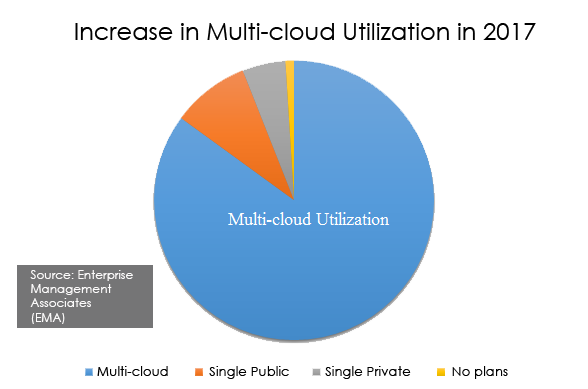
Multi-cloud adaptation:
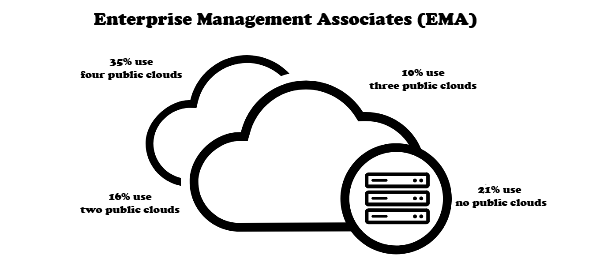
What an enterprise needs to incorporate multi-cloud models:
Let’s see what an enterprise needs to do to effectively use these computing models:
- Analyze data – determine the importance, priority and access frequency.
- Develop data management policies – to effectively leverage all kinds of enterprise data with the help of the previously collected information.
- Develop a professional IT team to deploy and follow the data management policies.
- Analyze the available private or public cloud services available in the market
- Deploy the solution as per the analysis and the policies.
Conclusion
A multi-cloud environment is made up of multiple public and/or private cloud environments. This model allows companies to overcome vendor lock-ins, improve cost effectiveness, and ensure availability and business continuity.
If you’re looking for a partner to help set up your own multi-cloud system, we have the expertise necessary to do so at an affordable price point that will work with your budget. Contact us today if you need assistance!









