Cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated and prevalent, putting sensitive data at risk. To combat these challenges, traditional password-based security measures are no longer sufficient. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) has emerged as a crucial solution to enhance data protection. By incorporating multiple authentication factors, such as passwords, and tokens, MFA adds an extra layer of defense against unauthorized access.
Understanding Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Different Authentication Factors: Strengthening Your Defense
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) employs a multi-layered approach to verify a user’s identity. These layers typically include three different authentication factors, offering increased security compared to single-factor authentication methods.
The factors are as follows:
- Something You Know: This factor requires users to provide information that only they should know, such as a password or a PIN. It serves as the first line of defense and is commonly used in various systems.
- Something You Have: In this factor, users need a physical or digital token to authenticate themselves. These tokens can be a smart card, hardware key, or even a mobile app generating one-time codes. It adds an extra layer of security by ensuring possession of a unique item.
Advantages of Using MFA in Modern Security Environments
Integrating Multi-Factor Authentication in modern security environments offers several significant advantages:
- Enhanced Security: MFA strengthens security by requiring multiple factors for user authentication. Even if one factor is compromised, the additional layers provide robust protection against unauthorized access.
- Reduced Risk of Identity Theft: MFA reduces the risk of identity theft, as hackers would need to bypass multiple layers of authentication to gain unauthorized access.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many industries and regions mandate the use of MFA to comply with data protection regulations, ensuring organizations meet necessary security standards.
- Simplified Password Management: As MFA provides alternatives to traditional passwords, users can enjoy simpler yet more secure authentication methods.
- Protection of Sensitive Data: With MFA in place, critical data stored in servers, storage systems, and backup and DR infrastructure remains shielded from potential cyber threats.
By leveraging the different authentication factors and embracing MFA, organizations can bolster their data protection strategies and safeguard their digital assets effectively.
Benefits of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Strengthening Security: Safeguarding Against Unauthorized Access and Data Breaches
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) stands as a powerful defense against unauthorized access and data breaches. By requiring users to present multiple forms of verification, MFA significantly enhances security and hinders cybercriminals from infiltrating systems and gaining control over sensitive information. Even if one authentication factor is compromised, the additional layers act as formidable barriers, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Mitigating the Risk of Password-Related Vulnerabilities
One of the primary advantages of MFA is its ability to mitigate the risk of password-related vulnerabilities. Traditional passwords alone are vulnerable to various attacks, such as phishing, brute force, and password reuse.
With MFA in place, even if a user’s password is compromised, malicious actors cannot gain entry without the additional authentication factors, providing a higher level of assurance.
Protecting Sensitive Data and Preventing Identity Theft
MFA plays a crucial role in protecting sensitive data stored within servers, storage systems, and backup and disaster recovery infrastructure. By implementing MFA, organizations ensure that only authorized personnel can access critical data, reducing the likelihood of data breaches and unauthorized information exposure.
Additionally, MFA helps prevent identity theft by making it significantly harder for cybercriminals to impersonate users and gain illicit access to confidential resources.
Safeguarding Business Reputation and Trust
MFA not only fortifies data security but also enhances the overall reputation and trust of an organization. In today’s digital landscape, where cybersecurity incidents can severely impact customer trust, implementing robust security measures becomes vital.
By demonstrating a commitment to protecting user accounts and sensitive information, businesses can instill confidence in their clients and partners, ultimately fostering stronger relationships.
Meeting Compliance Requirements
Many industries are subject to stringent regulatory standards that mandate the implementation of robust security practices, including the use of Multi-Factor Authentication. Compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and others often necessitates the adoption of MFA as part of a comprehensive data protection strategy.
Implementing MFA is a proactive step towards ensuring data protection, preserving business continuity, and instilling trust in users and stakeholders alike.
Use-Cases of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Secure Access to Corporate Networks and Cloud Resources
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) plays a pivotal role in fortifying the security of corporate networks and cloud-based resources, such as data storage, hyperconverged infrastructure, backup, and disaster recovery solutions.
By implementing MFA, organizations add an extra layer of protection to prevent unauthorized access to critical systems and sensitive data. Users are required to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as passwords, biometrics, or one-time passcodes, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access confidential resources.
In a corporate environment, where cyber threats are ever-evolving, MFA helps safeguard against phishing attacks, brute force attempts, and credential theft.
Additionally, when leveraging cloud-based solutions, MFA ensures that sensitive data stored in cloud repositories and applications remains protected, even when accessed remotely or from various devices.
Securing Financial Data with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
In today’s data-driven world, safeguarding sensitive financial data is of paramount importance. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) plays a crucial role in ensuring the security of stored financial information. By implementing MFA, organizations can fortify their data storage, hyperconverged, and backup and disaster recovery solutions to protect valuable financial data from unauthorized access.
MFA goes beyond traditional password-based authentication by adding additional layers of security, such as token-based authentication or biometric factors. This multi-layered approach minimizes the risk of data breaches and unauthorized entry, providing a robust defense against potential threats.
With MFA in place, businesses can confidently store and manage financial data in their storage appliances, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to this critical information. This level of protection bolsters compliance efforts and enhances the overall security posture of financial institutions and organizations dealing with sensitive financial data.
Enhancing Remote Access Security for Remote Workers
In today’s dynamic work landscape, where remote work has become more prevalent, the need for secure remote access is paramount. MFA offers a comprehensive solution to enhance the security of remote access for employees working from various locations and devices. This is particularly relevant to remote workers accessing company resources like servers, data storage, and cloud services from home or on-the-go.
By enforcing MFA, organizations can protect against unauthorized remote access attempts, securing corporate data and sensitive information from potential breaches. Employees may use one-time codes sent to their mobile devices, biometric authentication, or smart card-based verification, adding an additional layer of protection to their remote work interactions.
How to Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for OS Login and Administrative Tasks
With StoneFly’s advanced storage operating system, StoneFusion™, and virtualization engine, SCVM™, setting up multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a seamless two-step process. All StoneFly storage, hyperconverged, backup, and disaster recovery (DR), and cloud solutions come pre-installed with StoneFusion or SCVM, making MFA readily available across the board.
To enable MFA, ensure that StoneFusion is installed on bare-metal or SCVM is deployed on popular hypervisors like VMware, Hyper-V, KVM, Citrix (XenServer), or StoneFly Persepolis.
To enable MFA, Access the “System” menu, navigate to “Users,” and click on “Summary.”
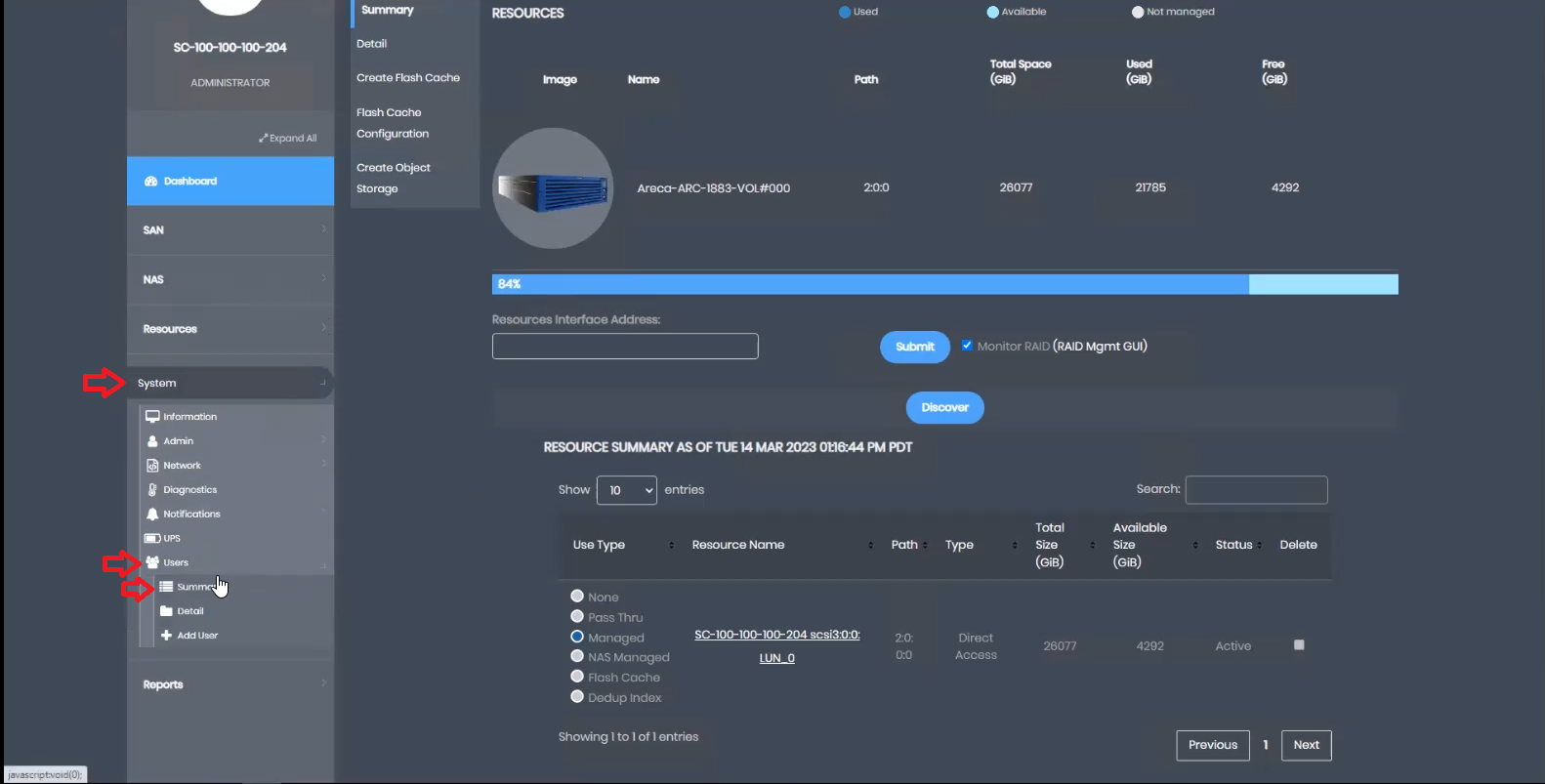
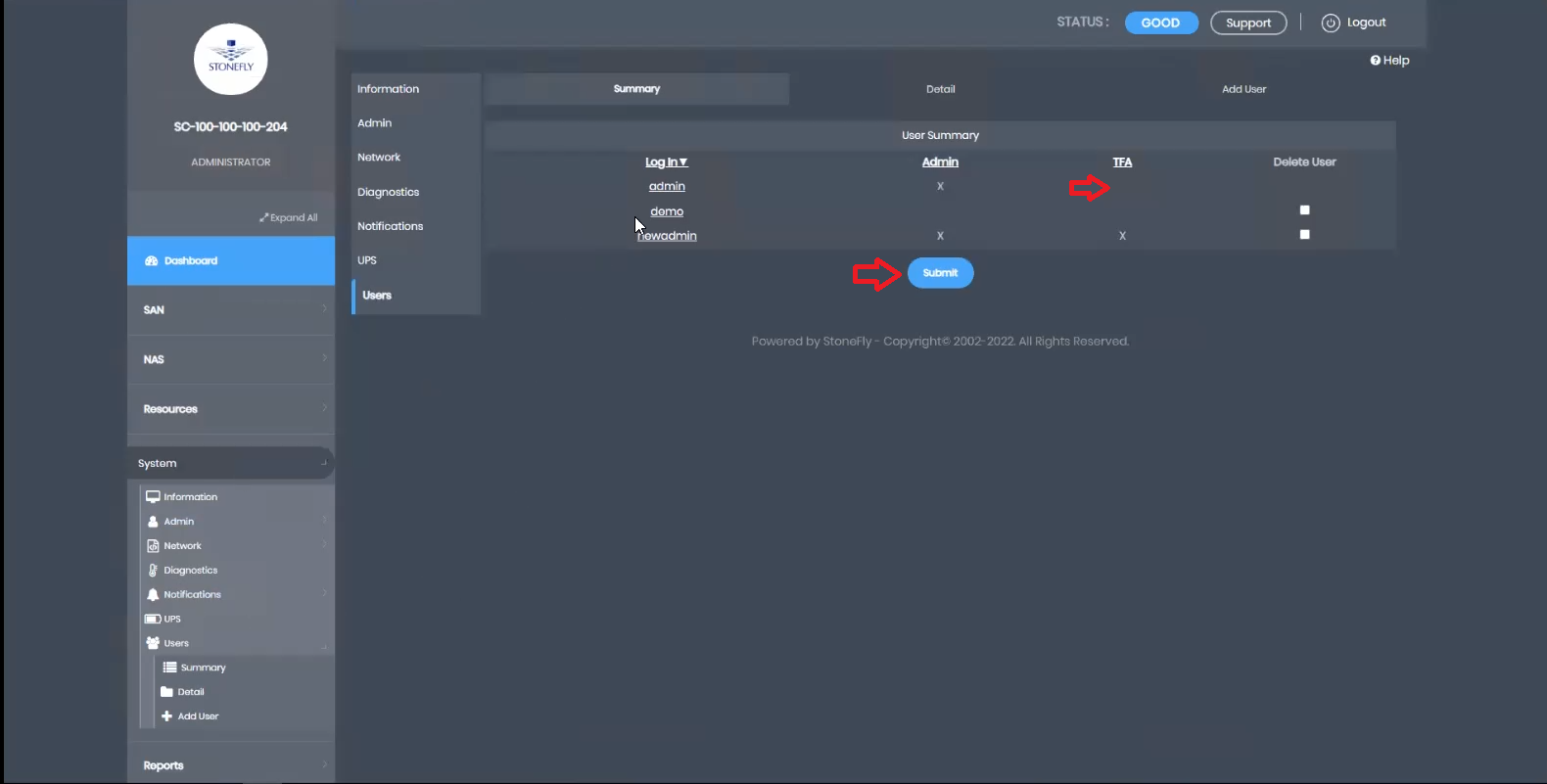
This robust security measure ensures that access to sensitive data and key operations requires multi-factor authentication, bolstering the overall security of StoneFly’s solutions.
Conclusion
In today’s evolving cybersecurity landscape, multi-factor authentication (MFA) has emerged as a crucial defense against unauthorized access and data breaches. With StoneFly’s innovative storage solutions, MFA becomes an integral part of securing sensitive data and critical operations. By implementing MFA, organizations can safeguard their stored data, protect against potential threats, and confidently embrace a proactive approach to data security.
Strengthen your data protection strategy today with StoneFly’s MFA-enabled storage, hyperconverged, backup, and disaster recovery solutions. Contact us to discuss your project(s).










