Properly sizing storage is a critical aspect of any IT infrastructure, but it becomes even more crucial when it comes to backup and disaster recovery. Veeam v12 is an excellent software for data protection, but to function efficiently, it requires the right amount of storage. The use of air-gapped and immutable repositories has gained popularity in recent times, as they offer added protection against cyber threats and ransomware attacks.
Air-gapped and immutable repositories are used to store Veeam backups, ensuring that even if the primary system is compromised, backups remain safe and secure. These repositories provide an extra layer of protection by isolating data from the rest of the network. However, the challenge lies in accurately sizing the storage needed for these repositories.
In this blog post, we will discuss the importance of properly sizing storage for Veeam v12, specifically when using air-gapped and immutable repositories. We will explore the benefits of these repositories, such as their increased resilience to ransomware attacks, and the challenges that come with them. We will also explain how StoneFly’s free storage calculator can help you plan for the right amount of storage needed for your Veeam backups, making it easier for you to ensure the safety of your data.
Why Air-Gapped and Immutable Storage is Important for Veeam v12
Air-gapped and immutable storage are becoming increasingly important for businesses that want to protect their data from cyber threats, particularly ransomware attacks. With the rise of such attacks, organizations are seeking more advanced backup methods to safeguard their data, and air-gapped and immutable storage has emerged as a reliable solution.
What is air-gapped storage?
An air-gapped storage repository is physically isolated from the network, meaning it is not connected to any outside source of data. This makes it an ideal solution for organizations looking to store critical data and applications that need to be protected from cyber threats and ransomware attacks. Air-gapped storage repositories are particularly effective against ransomware, as the malware is unable to infect the repository, and any data stored within it is kept safe and secure.
For more information about air-gapped backups, read What are air-gapped backups? How air-gapped backups work
What is immutable storage?
An immutable storage repository, on the other hand, is a type of storage that ensures data cannot be modified or deleted once it has been written. This means that any data stored within an immutable repository cannot be altered or destroyed by malicious actors, even if they gain unauthorized access. Immutable storage is particularly effective against ransomware, as it prevents hackers from altering or deleting backups, which can be crucial in restoring data after a ransomware attack.
For more information about immutable backups, read What are immutable backups and why are they necessary?
Why use air-gapped and immutable storage in combination
When air-gapped and immutable storage are used in combination, they provide a robust defense against cyber threats and ransomware attacks. An air-gapped and immutable repository ensures that data remains safe and secure, even if an organization’s network is compromised.
Air-gapped and immutable storage repositories are an essential component of a comprehensive backup and disaster recovery plan, especially in today’s world where cyber threats and ransomware attacks are on the rise. These repositories offer an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access and data tampering, as they physically isolate backup data from the primary network and prevent changes to/deletion of backup files.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using the StoneFly Air-Gapped and Immutable Storage Calculator for Veeam v12
StoneFly’s storage calculator is a useful tool for determining the right storage capacity for your Veeam v12 air-gapped and immutable repositories. There are three tabs on the calculator: Regular Repository, Immutable Repository, and Air-Gapped and Immutable Repository.
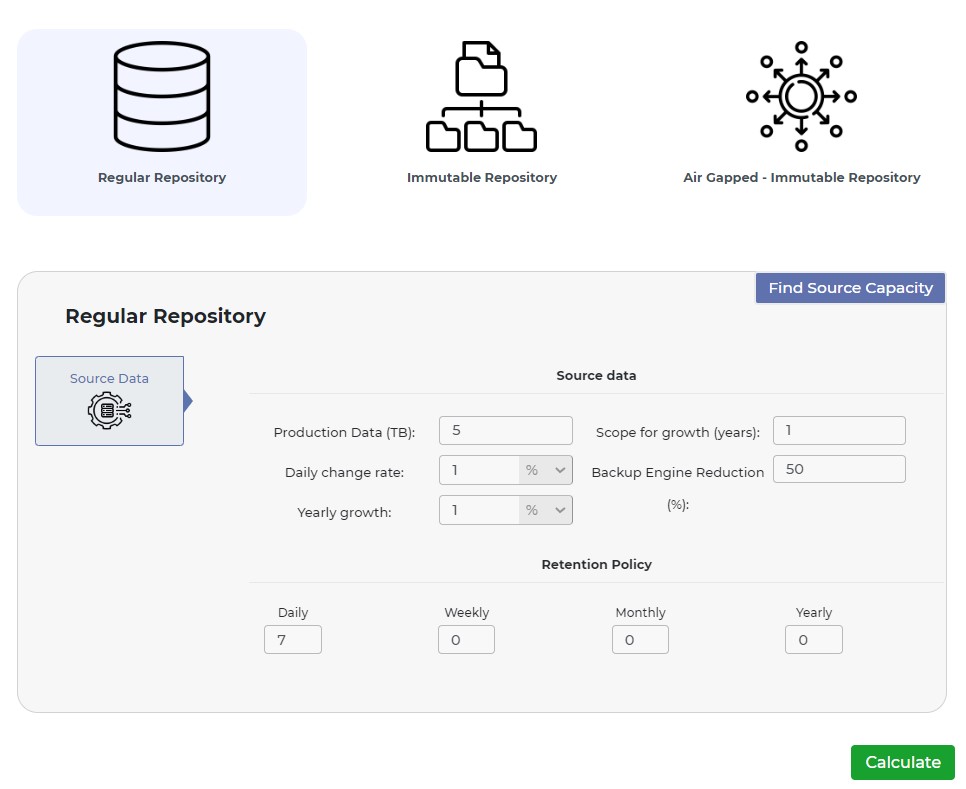
When using the Regular Repository tab, users need to enter the following information:
- Production Data (TB) – The amount of data that needs to be backed up.
- Daily Change Rate – The rate at which the data changes on a daily basis.
- Yearly Growth – The projected rate of growth for the data over a year.
- Scope for growth (years) – The number of years for which the storage capacity needs to be planned.
- Backup Engine Reduction – The expected rate of compression for the backup data.
Retention Policy – The length of time that the backups need to be retained, specified in days, weeks, months, and years.
When using the Immutable Repository tab, users need to enter the following information:
- Immutable Direct S3 ObjectLock – Check this if you are using an S3 ObjectLock storage repository that is immutable.
- Immutable Direct File Lockdown – Check this if you are using a file-based storage repository that is immutable.
Immutable Indirect File Lockdown – Check this if you are using a file-based storage repository that is immutable, and the StoneFly deduplication feature is enabled.
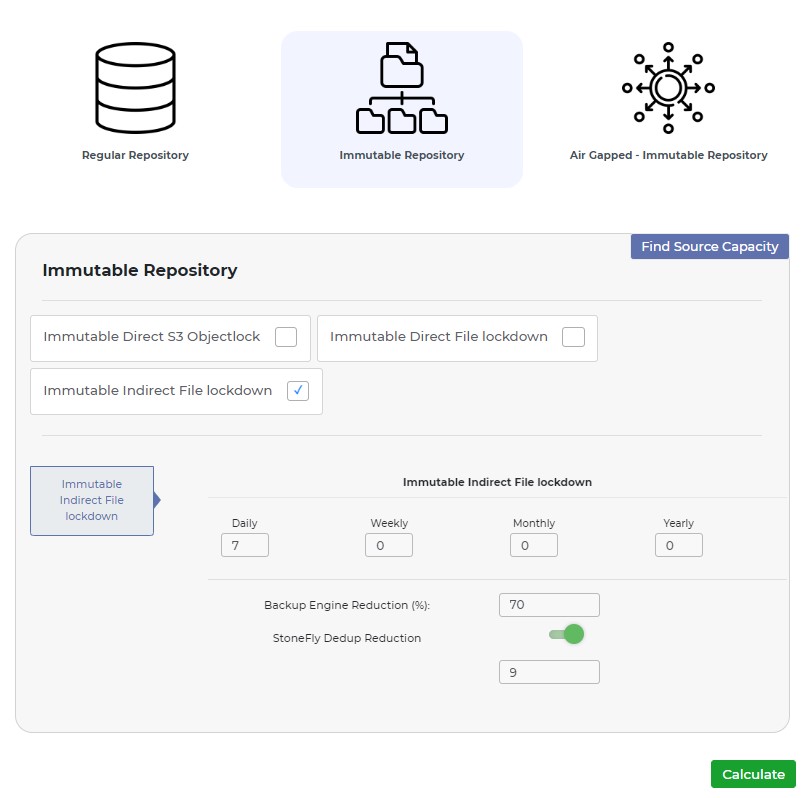
In the Immutable Direct S3 ObjectLock field, users will see the same retention policy options as in the Regular Repository tab.
In the Immutable Direct File Lockdown field, users need to enter the Backup Engine Reduction, enable/disable immutable gateway reduction, and retention policy in days, weeks, months, or years.
Immutable Gateway Reduction refers to the ability to reduce the storage capacity needed for immutable backups by leveraging intelligent gateway-based deduplication and compression.
In the Immutable Indirect File Lockdown field, users need to enter the Backup Engine Reduction, enable/disable StoneFly dedup reduction, and retention policy in days, weeks, months, or years.
StoneFly deduplication reduction is a feature that reduces storage space by identifying and eliminating duplicate data within backups.
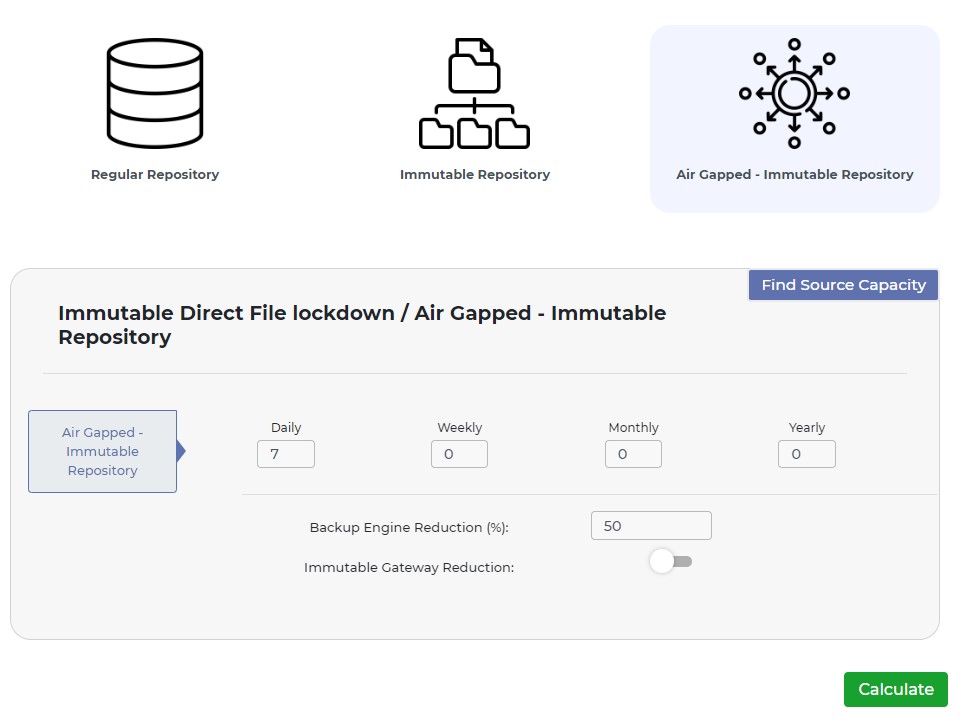
In the Air-Gapped and Immutable Repository tab, users need to enter the Backup Engine Reduction, enable/disable immutable gateway reduction, and retention policy in days, weeks, months, or years. This tab is for users who want to combine the benefits of air-gapped and immutable storage to achieve the highest level of data protection.
Bulletproof Your Backups: Tips for Using Air-Gapped and Immutable Storage with Veeam v12
Air-gapped and immutable storage solutions offer additional protection against cyber threats and ransomware attacks, by isolating the backup data from the primary environment and making it unalterable. When setting up air-gapped and immutable storage in Veeam v12, there are several best practices to keep in mind.
These include selecting the appropriate storage media and replication mechanisms, using the latest software updates and security patches, implementing access controls and monitoring tools, and regularly testing the recovery process to ensure that backups can be restored when needed.
- Implement a tiered backup strategy: A tiered backup strategy can help you maintain multiple copies of your data in different locations, including offsite air-gapped storage. By storing backups on different types of media, such as disk, tape, and cloud, you can protect against various types of failures and cyber threats.
- Follow the 3-2-1 rule: The 3-2-1 rule states that you should keep at least three copies of your data, store them on two different types of media, and keep one copy offsite. Following this rule can help you maintain reliable backups that are safe from cyber-attacks.
- Use multiple air-gapped storage devices: To ensure maximum protection against ransomware attacks, it’s recommended to use multiple air-gapped storage devices. This way, if one device becomes infected, you will have a backup that is not affected by the attack.
- Implement multi-factor authentication: Enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) for each module of your backup and recovery systems, including production, network, and air-gapped controller, can help protect against unauthorized access to your data, making it a critical component of air-gapped and immutable storage implementation.
- Use sandbox environments for backup and DR testing: Before implementing backup and disaster recovery procedures in a production environment, it’s best to test them in a sandbox environment. This way, you can ensure that your backups are properly configured and will function correctly in the event of a disaster. This is especially important for air-gapped and immutable storage implementations, where there may be limited access to backups once they are stored.
- Implement a ransomware scanner: Using a ransomware scanner can help detect and prevent ransomware attacks on your backups, including dormant and sleeper ransomware. By proactively scanning your backups, you can ensure that they remain secure and reliable for restoration in case of a ransomware attack.
Conclusion
In conclusion, properly sizing air-gapped and immutable storage is crucial to protect Veeam v12 backups against cyber threats and ransomware attacks. By using StoneFly’s storage calculator, you can ensure that you have the right storage capacity to meet your needs.
Remember to regularly test your backups, follow the 3-2-1 rule, and consider implementing multi-factor authentication, sandbox testing, and ransomware scanners to further enhance your backup security. With these measures in place, you can have peace of mind knowing that your data is safe and can be easily recovered in case of any emergencies.










