In other words, these storage solutions facilitate the creation of a comprehensive, reliable and efficient storage solution.
The Three Storage Levels: File, Block & Object
Storage levels are basically three ways of how data is handled when storing it. Each storage level stores data differently and the stored data is utilized and accessed differently. Based on these differences, each storage level best suits a specific kind of data storage requirement.
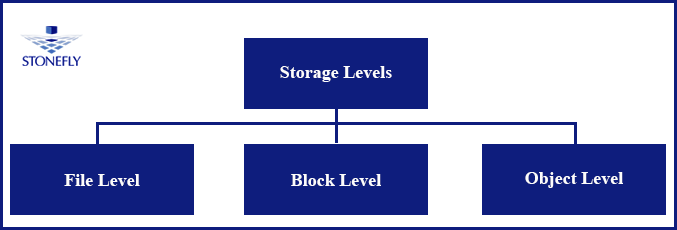
As depicted in the image, there are three types of storage:
- File Level.
- Block Level.
- Object Level.
File Level Storage
File storage is a hierarchical way of storing files. An individual file is accessed using the path or address of the file. Attributes associated with the file such as its owner, who has access to the file and size of the file are stored in the metadata of the file system. It’s a simple system to use and implement. In comparison to
The NAS storage stores the files and hosts them over a local network constituting a file sharing system with reduced latency as compared to cloud storage solutions. If the data requirement of the enterprise is to share files between departments located on the same premises or building, then a NAS is a better option than enterprise cloud storage. This is because NAS hosts the files over a local network, keeping the data close and easily accessible as compared to cloud storage.
Block Level Storage
Block level storage divides the data into chunks called blocks. The collection of multiple chunks leads to the generation of a specific file. A block is accessed by generating
In block level, the only relevant metadata is the address to the block and arguably even that is not exactly metadata. Individually, a block has no description or ownership related to it; hence it makes little sense by itself. It only makes sense when combined with other chunks of data like itself to form a complete file or data.
This granular level storage is deployed in Storage Area Network (SAN) environments. Besides the difference of how file level and block level handle data, there’s also a fundamental difference in the utilization of the two. NAS appliances, that utilize
Object Level Storage
Objects combine the data with its metadata. This bundle or object is assigned an ID. The ID is generated versus the content of the object. This ID is used to call or access the object when needed. File level storage stores files in a hierarchical structure; however, object storage utilizes flat structure to do so. An object within this architecture can be called using this ID regardless of the location, it can either be in the local storage or stored in a geographically separate location. The beneficial feature unique to object level storage is that it facilitates users to define the attached metadata of an object. This enables vast opportunities for data analytics and efficient storage management. Object level storage is used in cloud
Configurations of each Storage Level/Mode
The
- Standalone configuration.
- HA (High Availability) configuration.
Scale out configuration.

Standalone Configuration
As the name suggests, there’s only a single chassis involved. The chassis has hard drives, SSDs, RAID controllers making it a complete storage.
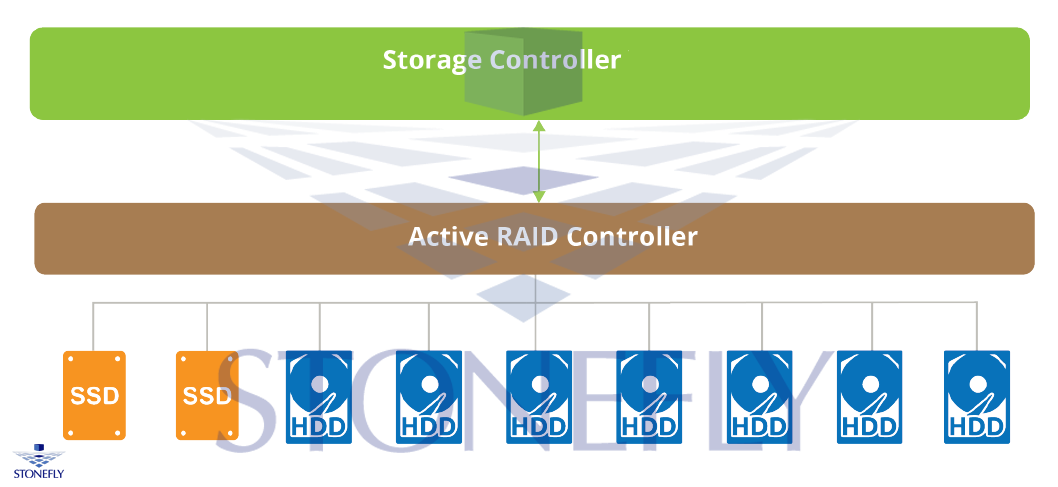
StoneFly Integrated SAN Storage products are an example of this configuration mode. It is
High-Availability (HA) Configuration
This configuration ensures high availability by having twin systems working simultaneously. This prevents downtime or disruption in
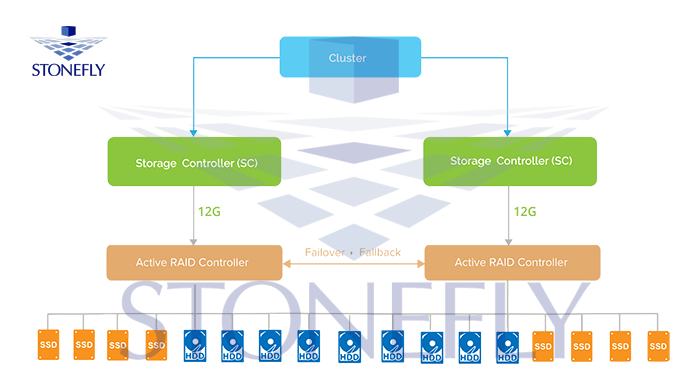
StoneFly provides two appliance families in this configuration: Voyager and Flash Voyager DX Series. These appliances come with a fully modular design with no single point of failure. The appliances are equipped with two clustered redundant storage controllers. Each storage controller starts with 16 scaling up to 44 Parallel storage core engines. This modular design is extremely robust and scalable to meet any demanding workload. And as with the previous appliances, these appliances also facilitate cloud connect services. This
Scale out Configuration
In this configuration, it’s not one or two storage controllers; it’s many of them. This implies that if you need improved performance or more storage capacity, you acquire multiple nodes.


referred to as scaling up. With StoneFly’s appliances, you get to scale out. Scaling out is the addition of additional nodes. The advantage of node addition as compared to expansion units, this scaling out improves performance and capacity due to the workload being distributed among the nodes.
Summary
There are three types of storage levels: File, block










