Unstructured and structured data are two of the most common data structures business owners create, process, and store. A better understanding of the two enables data owners to select the right data storage infrastructure and effectively leverage their business data.
In this section, we take a closer look at structured and unstructured data, what they are, and the differences between them.
What is Structured Data?
Structured data, often categorized as quantitative data, is the type of data that has been formatted to fit a set structure. Its make-up makes structured data easier to work with and faster to search.
Examples of Structured Data
Commonly structured data is generated by relational databases such as MySQL, Oracle, etc. Database applications that make use of structured data include inventory management systems, sales transactions, airline booking systems, bank transactional systems, CRM applications, accounting systems, etc.
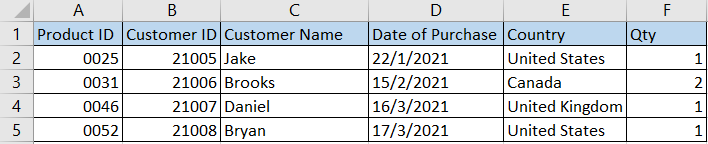
(Structured data example: Excel sheet with information about customers and their purchases)
Pros and Cons of Structured Data
| Pros | Cons |
| Requires less processing in comparison to unstructured data and is easier to manage. | Limited usability because of its pre-defined structure/format |
| Machine algorithms can easily crawl and use structured data which simplifies querying | Structured data is stored in data warehouses which are built for space saving but are difficult to change and not very scalable/flexible. |
| As an older format of data, there are several tools available for structured data that simplify usage, management, and analysis |
Looking for a storage appliance for your structured data? Check out StoneFly SAN appliances.
What is Unstructured Data?
Unstructured data, often categorized as qualitative data, is the type of data that is stored in its native format and is not processed until it is used or needed. Compared to structured data, unstructured data is more abundant and comes in a greater variety of formats.
Examples of Unstructured Data
Pros and Cons of Unstructured Data
| Pros | Cons |
| Variety of native formats facilitate a greater number of use-cases and applications | The greater number of formats makes it equally challenging to analyze and leverage unstructured data. |
| As there is no need to predefine data, unstructured data is collected quickly and easily. | The large volume and undefined formats make data management a challenge and specialized tools a necessity. |
| Unstructured data is stored in on-premises or cloud data lakes which are highly scalable. | |
| Although challenging, the greater volume of unstructured data provides better insights and more opportunities to turn your data into a competitive advantage. |
Looking to store your unstructured data? Check out our highly scalable NAS appliances or get cloud storage in Azure, AWS, or our private cloud.
Difference Between Structured & Unstructured Data
| Structured Data | Unstructured Data | |
| Formats | Several formats | Huge number of formats |
| Data Model | Predefined/not flexible | Varied/flexible |
| Storage | Data warehouses | Data lakes |
| Databases | SQL, Oracle, Relational databases | NoSQL, Non-relational databases |
| Nature of data | Qualitative | Quantitative |
| Search | Easy to search | Difficult to search |
Looking for a unified storage for your structured, unstructured, and object data? Check out StoneFly unified storage appliances.







