As the technology is advancing at an exponential rate and so is the ransomware which has become a serious epidemic in the recent past adversely affecting businesses of all shapes and sizes. Protecting your business is a serious ‘business’ now, more than ever before. According to a U.S interagency report, there have been 4000 daily ransomware attacks since 2016. The increase is not limited to just the number; the attack continues to become more lucrative and more sophisticated.
Understanding Ransomware
Ransomware is malicious software that gains control over the system by encrypting files, locking the computer and then retaining the control until the user agrees to pay ransom. Generally Ransomware appears in the following forms:
- By encrypting files to stop users from opening them.
- By locking the screen with a webpage of a full screen image to prevent user from accessing the PC
Most ransomware types follow the following key components while keeping their uniqueness from case to case.
- Infecting through email: Although some ransomware might get hold of the victim’s computer via drive-by download advertising, malicious websites or peer-to-peer network file sharing, however most of the time email medium is used to accomplish this. The end user is tricked into opening an email having attachments with enticingly common names. The attachment is usually a zip file containing an .exe which gets downloaded into the target computer and the application runs by adding a key to the windows registry.
- Covert communication: After the download, a connection is established between the malware and the command and control server. Most modern ransomware rely on domain generation algorithm to avoid detection as it hops between new servers in an organized manner.
- Advanced Encryption: Once the server connection get established, the malware generated a pair of encryption keys one of which is public and the other is private. Mostly the key is generated using RSA-2084 bit encryption algorithm and military-grade 256-bit AES encryption.
- Demanding the Ransom: Cybercriminals then demand Ransom in the form of Bitcoins or some other not easily detectable mode of payment in exchange for the key to unencrypt infected files.
- Meeting the deadline: Constant reminder is given to the victim in the form of a popup window, constantly appearing on their screens with the timer mentioning the time left before the private encryption key is destroyed and the files are lost forever.
Ransomware Defenses
User Education
Educate your employees about the types of malware, especially ransomware as it is the most prevailing one these days. Make them aware of popular tactics and social engineering methods by sharing sample emails with them so they don’t fall victim to phishing emails with malware attachment or spoofed messages. However user education is useful but not sufficient to win this battle.
Constantly Update Antivirus, Anti-Malware Software and Operating Systems
Using the traditional anti-virus and anti-malware software can be a bit dangerous as today’s malware is very dynamic and has the ability to changes itself after each attack; hence becoming more undetectable and unpredictable. Therefore it is required to always have an advanced anti-malware system that uses heuristic techniques based on decision rules or weighing criteria. The advanced variant works by analyzing and defending previously unknown instances and different types of malware, especially ransomware. However, no matter how advance the anti-malware is, it can still not be labelled as completely bullet proof as developers of malware are smart enough to detect and bypass certain heuristic techniques as well.
Set Up a Next-Generation Firewall
A next generation firewall can be helpful in combating numerous threats. Some of them are even able to detect zero-day threats before they infect the system. Firewalls also are helpful in making the SMB (Server Message Block) more proactive about defense against ransomware instead of a reactive approach after the attack.
BACKUP the Data
No matter how much you educate your employees or how powerful your anti-malware software and firewall is, you can never guarantee complete safety of your business owing to dynamic nature of ransomware. Therefore it is required to back up your data offsite. Why offsite? Because local backups get encrypted easily and you will have to pay the ransom to get your data back.
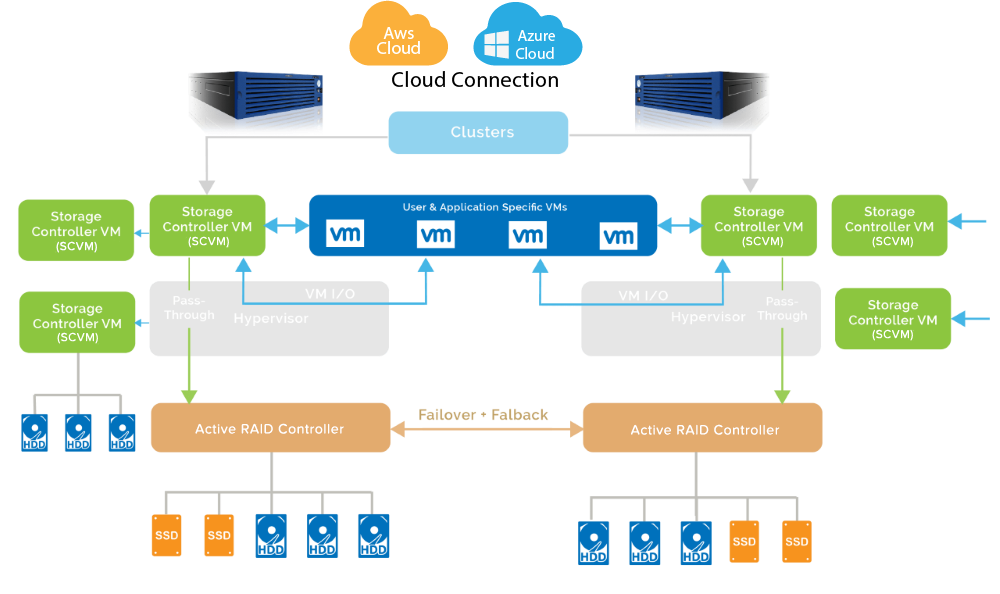
To overcome this problem, Stonefly has come up with a complete solution; Dual Node stretch Hyper-converged Cluster using which you can backup all of your physical/virtual servers/workstations and manage all of your backup operations for your data center or office with a single central management console. In this Cluster, each node is completely independent shares no memory, disk storage, network, CPU, power supply making it all fully virtualized. If one node fails, the other will pick up the pace, offering always-on, continuous support to your enterprise.
What makes this solution all the more desirable is that the main storage HDD and SSD disconnects itself from the appliance if it detects a threat making it less likely for you to fall prey to Ransomware. In addition, the solution offers a lot of features for your enterprise to choose from and customize them according to your requirement. Following are some of them:
- Replication – Asynchronous Replication to a remote site or to the cloud allows your Virtual Machines and data to be stored and protected off-site.
- Automated Snapshots: for maintaining periodic versions of your data to ensure complete safety because an infected file might as well get backed up. With versions, it is easier to get to the clean copy of the data.
- Compression and deduplication: optimizes utilization of the network and storage. The volume of backup data can be reduced by up to 90% and maximizes backup speed.
- Automatic backup validation: can be manual or scheduled as per user’s choice.
- Scale out: to as many as nodes you need for capacity and performance. There is no limitation to the number of the nodes in Scale Out configuration.
- Storage transportability: for data transfer, backup or general security.
Steps to Recover from Ransomware
In spite of taking all the precautionary measure, if ransomware still hits your enterprise, immediately perform the following actions or contact Stonefly team to help you execute them effectively:
Disconnect from the network and stop backing data up immediately
Although the primary storage is disconnected automatically, you are still required to manually disconnect the infected machine from the network as some ransomware variants encrypt shared files on the network in order to ensure complete safety. When you stop backing up the data, you will be stopping the malicious software from overwriting clean backups with infected files. After this, look again for infected systems, if any.
Remove ransomware and clean computers of malicious software
Remove all the traces of ransomware using appropriate malware remover before doing any restore operation. DONOT recover data until the malware is completely gone. At this point you should not worry about paying the ransom or impatiently restoring the data, your data is safe with us, at multiple locations with multiple versions. Before the final restore, conduct a test run in safe mode on the network to make sure there are no infected files left.
Restore from the most recent clean backup
Locate the cleanest version of your latest data and Restore to enjoy the business continuity without having to pay any Ransom.