Disaster recovery has gained utmost importance in the modern world with increases in various natural or manmade disasters. There is a need to move forward in the world of advanced technology to make sure that the business remains updated and on par with data protection. Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) has developed extreme importance in the innovative world of technology.
Let’s examine the following scenario, a tenant wishes to use VM replication to implement a disaster recovery strategy, and for this purpose, the tenant contacts the SP. To onboard the tenant, the SP needs to create an account for the tenant, and after creating the account, Veeam cloud connect will deploy a VM network extension appliance at the SP network and in this example with IP 20. This network extension appliance will be used as a virtual router to create routing between tenant subnet which is VLAN 33 and the SP network and also to establish a VPN connection with a tenant site. To keep tenants separated from each other Veeam will host each tenant within a VLAN.
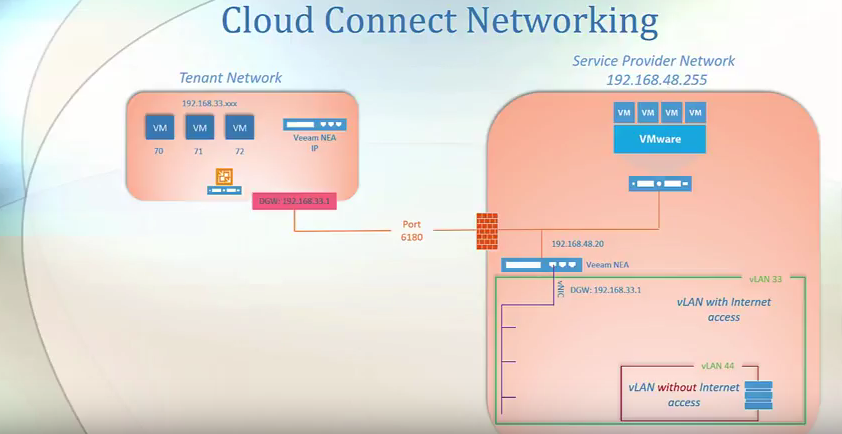
In Veeam backup and replication appliance the SP can specify the VLANs with internet access and VLANs without internet access. VLANs without internet access can be used as internal networks that let VM replicas communicate to each other after full-site failover and to production VM’s after partial site failover.
Once the SP creates and shares the tenant account, the tenant will use console to connect to the SP disaster recovery as a service offering and once the connection is established, the attendant network extension appliance will be provisioned at the tenant network. By default, the communication port between the tenant and the SP uses a TCP port number 6180, and in case of disaster recovery as a service, the SP must configure the firewall to open for TCP and UDP traffic on that port. Once the communication is stabilized, the tenant will be able to create a replication job to replicate the VMs to the SP datacenter.
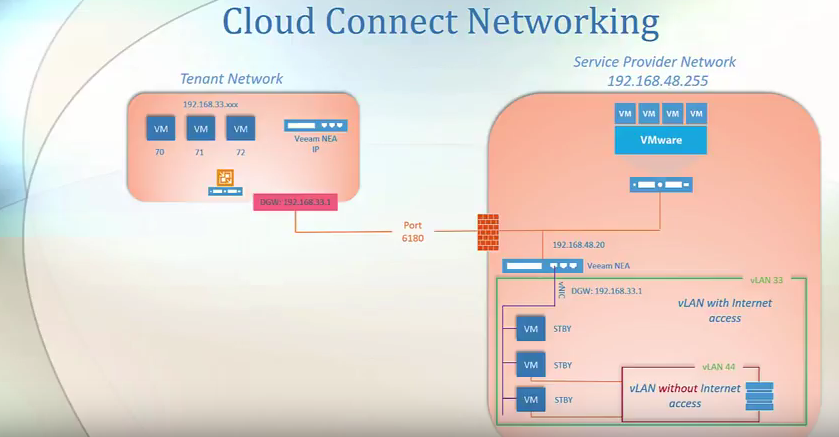
In this example, the tenant replicates three virtual machines among which two of these virtual machines are connected to a V-LAN without internet access as they share a database or a storage using a private network. Also note that all of the virtual machines are part of a V-LAN with internet access. After the data replication, virtual machines are provisioned on a standby state.
The remediation from data disaster using Veeam cloud connect is faster as compared to other solutions. Let’s discuss an example of a disaster in which there is a loss of a single workload or a single virtual machine which is also known as partial failover.
- Partial Failover
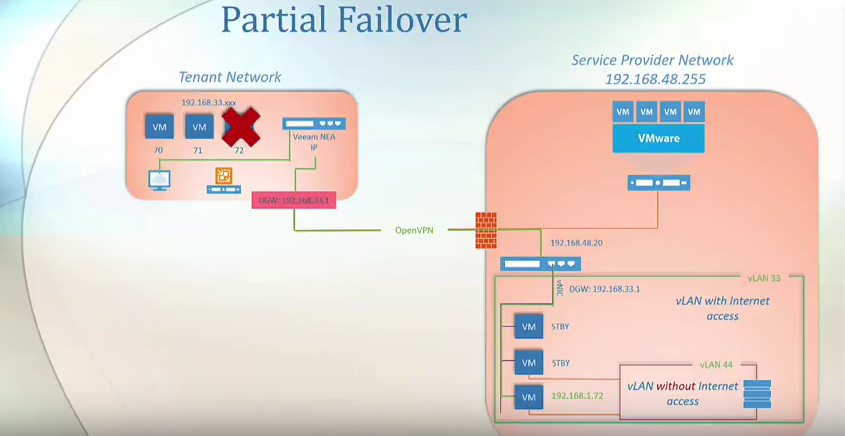
The tenant network extension appliance will start, the tenant network extension appliance at the SP will be started. The failed VM replica at the SP side will start which is 72, and a VPN tunnel will be established between the tenant and the SP network extension appliance. The user will reconnect to the application through the VM network extension appliance at the tenant network.
- Full-Site Failover
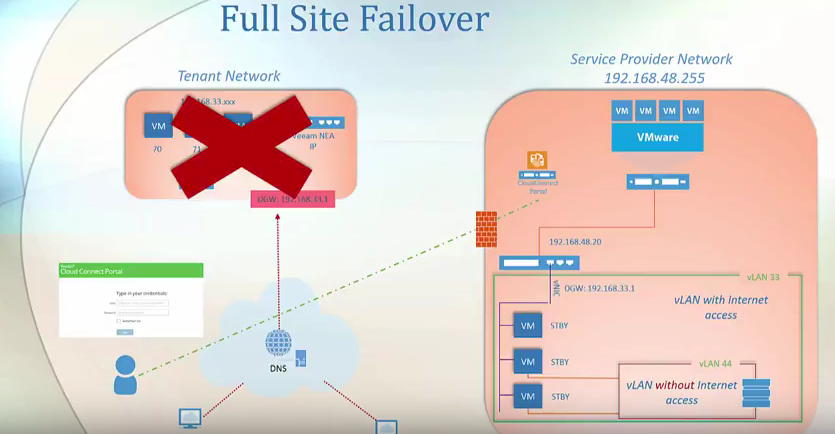
Full site failover process will start at the SP side by starting the VM network extension appliance and all the virtual machines. After it, a public IP address will be published for the external users to reconnect to the tenant workload running from the SP network.