Interaction between two enterprises for the first time raises trust concerns. Regardless of the type of transaction between the two; it can be of financial nature or it can be an exchange of code or software between two IT industries.
What is Block-chain as a Service (BaaS)?
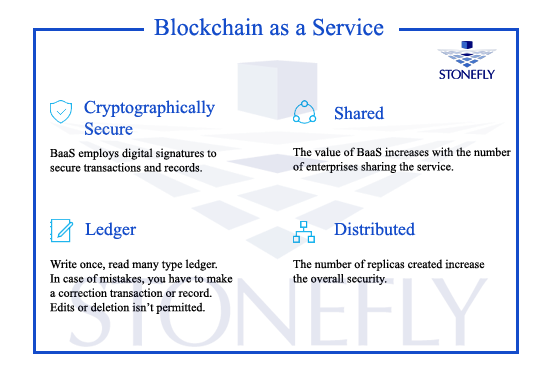
BaaS is a maintenance database that manages blocks. Blocks are continuously growing list of ordered records. Each block comprises of a timestamp and a link to a previous block. Block-chains are designed to resist any changes in the data, once it has been recorded. The block-chain database management is autonomous due to the use of peer to peer network and a distributed time stamping server. Although BaaS is associated with efficient and verifiable transaction; it has many other applications. BaaS is capable of recording events, medical records and identity management, and providing data provenance.
How Block-chain as a Service (BaaS) works?
Consider the conventional means of trading. Normally, you have to pay in advance and then you get the product. This leaves the possibility open that the vendor can choose not to send the product and keep the money. This leads to the intervention of third party service providers such as Ebay, Paypal etc. The utilization of third party service providers is somewhat reliable; however, this leads to their cut of the transaction, meaning additional costs.
Block-chain removes the necessity of a third party service provider and makes trading a reliable process. With BaaS, you can utilize something called smart contract. Instead of paying directly to the second party, you can hold the money in the smart contract. The contract informs the vendor that the amount has been submitted to the contract and then the vendor sends the product to you. After receiving the product, you digitally sign the contract confirming the delivery and the payment is processed. If the vendor doesn’t send your product and the money remains in the smart contract, it is returned after a week. So the liability of losing your money or the risk of not receiving the product is eliminated.
BaaS decentralizes the flow of data. There are numerous benefits of decentralization and the alteration to fundamental processes and models.
Benefits of BaaS & Decentralization

- Eliminates Intermediaries: With a reliable mean to make transactions or move data, there is no need of third party service providers to ensure transparency. This enables companies to redesign their business model and utilize the previously dedicated resource elsewhere.
- Reduces Fraud: The data storage in BaaS doesn’t permit any deletion or edits. It is write once and then read many principle. This makes it very secure and transparent, making it nearly impossible to change records.
- Improves Efficiency & Speed: BaaS simplifies transactions and processes facilitating reduced settlement times. This improves efficiency and speed of overall operations.
- Increases Revenue & Savings: Removal of intermediaries leads to redesigning of business model and to savings. This opens the door to increased revenue as well.
- Reduce Counterparty Risk: With the help of smart contracts you can process “trustless” transactions between multiple parties.
Conclusion
Block-chains offer a great way for information sharing for enterprises and various industries. Microsoft’s Blockchain as a Service cloud computing platform is flexible, scalable and supports a rapidly growing number of distributed ledger technologies. You can make transactions without having to worry about trust issues; this provides numerous benefits to the enterprise. Block-chains are normally associated with the facilitation of transactions; however, its experts agree that it has the potential to play a vital role in various industries other than the finance industry as well.









