This month we will be discussing best practices for enterprise IT environments to leverage Veeam Backup and Replication software for enterprise data protection, high availability and data recoverability. This is the first article of the series dedicated to the best practices related to backup proxies.
Before we discuss the best practices, let’s briefly define backup proxies and the services and components that make up Veeam backup proxies.
What is a Backup Proxy?
A backup proxy is a bridge-like architecture component that connects the backup server with the other components of the backup infrastructure. As the backup server administers tasks, the backup proxy processes backup jobs and delivers traffic.
The basic operations of a backup proxy include:
- Retrieving Virtual Machine (VM) data from the production storage.
- Source side in-line data deduplication to skip whitespace and redundant blocks reported by vSphere CBT (Change Block Tracking) or Veeam File Change Tracking (FCT) or Microsoft Hyper-V.
- Storage encryption (AES 256-bit, if enabled)
- Send the data to a backup repository (For instance, when running a backup job) or another backup proxy (For instance, when running a replication job).
About Veeam Backup Proxy Services and Components
The following are the services and components that make up Veeam backup proxy:
- Veeam Installer Service – This is a service that is deployed on the Windows server once it is added to the list of managed servers in the Veeam backup and replication console. The service analyses the system and installs and upgrades necessary components and services.
- Veeam Transport Service – This service is responsible for deploying and coordinating executable modules that act as data movers. The service performs main job activities on behalf of Veeam backup and replication (communicating with VMware tools, copying VM files, performing data deduplication and compression and more)
- exe process – This is a data mover component that can be initiated multiple times (whenever necessary) for each data stream on the backup proxy. These processes can operate two modes: read or write. When used on a proxy server for backup, they are only performing read operations, while “write” mode is used for writing data on a target proxy (replication).
Best Practices for Backup Proxies
Users can easily utilize backup proxies to scale Veeam backup infrastructure based on the organization’s requirements. In terms of deployment, IT environments have two options:
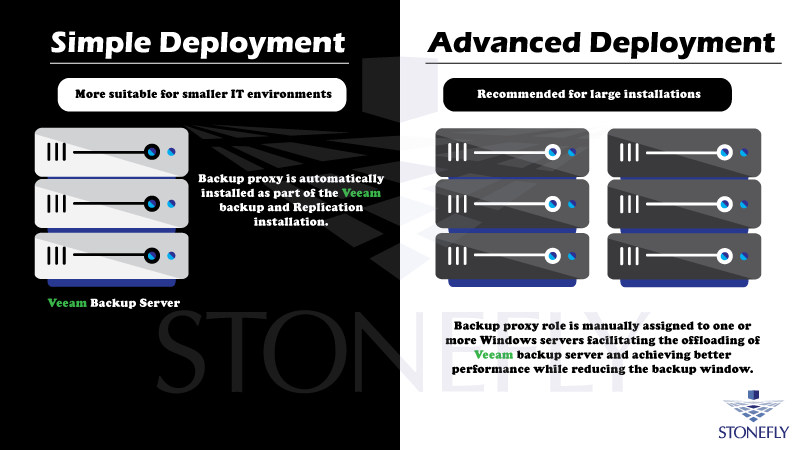
Simple Deployment
For smaller IT environments, the backup proxy is automatically installed on the Veeam-ready backup server as part of the Veeam backup and replication installation and is sufficient.
Advanced Deployment
In an advanced deployment, the backup proxy is manually assigned to one or more Windows servers. This facilitates offloading the Veeam backup server, achieving high performance, and reducing the backup window. That is why for large installations, it is recommended to deploy dedicated backup proxies
Backup proxies are deployable in the primary site, where backup servers are located, or in a remote site where additional infrastructure needs backup. Backup proxies can be installed on any managed Microsoft Windows server added to the backup infrastructure. The transport modes for the backup proxy depend on whether the proxy server is installed on a physical or virtual machine.
As mentioned earlier, the backup proxy handles data traffic between vSphere or Hyper-V infrastructure and backup and replication during backup, replication, VM migration jobs, VM copy or VM restore. Backup proxies are also used to detect and scan snapshots to enable Veeam Explorer for Storage snapshots features when any primary storage is added to the backup server.
In other words, a backup proxy facilitates a light-weight transport service that takes a few seconds to deploy. When users add a Windows-based server to Veeam backup management console assigning the backup proxy role to it, Veeam backup and replication installs the necessary components and starts the required services on that server. Any host in a Hyper-V cluster is automatically enabled as proxy server, when it’s added to the infrastructure. With built-in Intelligent Load Blancer (ILB), each time a job starts the backup server manages dispatch of tasks to proxy servers.
Intelligence Load Balancing (ILB) using Max Concurrent Tasks
IT environments can specify a threshold for proxy load using the Max concurrent tasks proxy setting (where a single task stands for a VM disk). Veeam backup and replication uses a load balancing algorithm to automatically spread the proxy load across multiple proxies. This feature facilitates users to minimize backup time windows, increase backup performance and optimize data flow.
At installation, the proxy server is configured for two simultaneous tasks by default while the subsequently added proxy servers analyze the CPU configuration. Automatically, the proxy server proposes to configure 1 task per CPU core. During deployment, users choose the data stores the proxy can access. This information is stored in the configuration database. At backup time, this information is used to automatically select the best transport mode depending on the type of connection between the backup proxy and data store.
First, Veeam backup and replication checks if data processing can be assigned to a backup proxy with the following proxy:
- Direct Storage Access (includes VDDK based Direct SAN or Veeam proprietary Direct NFS)
- Virtual Appliance mode (Hot-add)
- Network Block Device (NBD)
After the algorithm identifies all existing backup proxies it allocates tasks using the built-in Real-time Scheduler (RTS):
- The algorithm discovers the number of tasks being processed at the time by each proxy and looks for the server with the lowest load and the best connection.
- All tasks are included in the “VMs to process” queue. When a proxy task slot becomes available, RTS automatically assigns the next VM disk backup in queue to it.
- In terms of priority, the disk that belongs to a processed VM has higher priority while the VMs of already running jobs have the next higher priority.
Note: At the backup repository, only one thread writes to the backup storage per running job. If few jobs with a higher number of VMs are processed simultaneously, users may experience that these threads cannot fully utilize the available backup storage performance. Users can also consider enabling per VM backup files in the event the throughput per I/O stream creates a bottleneck.
Note: Default recommended value is one task per core/vCPU, with at least 2 CPUs. To optimize the backup window, users can cautiously oversubscribe the Max concurrent tasks count but they need to monitor CPU and RAM usage carefully.
Storage Optimizations with Veeam Advanced-Data Fetcher (ADF)
Stock VDDK (Virtual Disk Development Kit) transport modes have a number of limitations, such as the inability to process multiple disks in parallel when using Virtual appliance transport mode (hot-add) thereby introducing excessive VMFS metadata updates, when performing replication, or being unable to backup from NFS based datastores. Veeam developed a logic to bypass VDDK and overcome these limitations when it is more optimal to do so.
Veeam ADF adds increased queue depth for >2x read performance on enterprise storage arrays. ADF is supported for backup from storage snapshots, Direct NFS and virtual appliance mode.
Other optimizations include:
- Allow restore via Direct SAN.
- Proprietary NFS client for VM backups on NFS datastores.
- Bypass VDDK when using replication or VM restores using hot-add, to prevent excessive VMFS metadata updates.
- Parallel processing of multiple Virtual Machine (VM) disks during restore.
- Parallel processing of multiple Virtual Machine (VM) disks, when backing up via hot-add.
Parallel Processing of VMs/VM disks
StoneFly’s Veeam backup and replication appliance allows parallel processing of VMs/VM disks:
- It can process multiple Virtual Machines (VMs) within a job simultaneously, increasing data processing rates.
- If a VM is created with multiple disks, Veeam will process these disks simultaneously to reduce backup time and minimize VMware snapshot lifetime.
- RTS prioritizes currently running parallel processes for Virtual Machine (VM) disk backups.
In order to achieve the best backup window, it is recommended to oversubscribe the tasks slots, and start more jobs at the same time. This enables Veeam to leverage the maximum of the task slots and lead the process into an optimum backup window.
That concludes our recommendations for the best practices pertaining to backup proxies. Subscribe to our newsletter and keep an eye out for the upcoming best practices article about Veeam backup and replication in the series.
![Veeam-BR-Best-Practices[1]](https://staging.stonefly.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/Veeam-BR-Best-Practices1.jpg)












